Inference via the Wallaroo MLOps API
Table of Contents
Inference Requests via API
Retrieve Inference Endpoint API Spec
The method wallaroo.pipeline.Pipeline.generate_api_spec() returns the pipeline inference endpoint specification yaml format under the OpenAPI 3.1.1 format. This provides developers the ability to import this yaml file into their development environments and have:
- Inference API endpoint(s).
- Inference endpoints require authentication bearer tokens. For more details, see Retrieve Pipeline Inference URL Token.
- Input fields and data schemas.
- Output fields and data schemas.
Retrieve Inference Endpoint API Spec Parameters
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | String (Optional) | The file path where the yaml file is downloaded. If not specified, the default location is in the current directory of the SDK session with the pipeline name. For example, for the pipeline sample-pipeline, the endpoint specification inference endpoint file is downloaded to ./sample-pipeline.yaml. |
Retrieve Inference Endpoint API Spec Returns
A yaml file in OPenAPI 3.1.1 format for the specific pipeline that contains:
- URL: The deployed pipeline URL, for example, for the pipeline
sample-pipelinethis URL could be:https://example.wallaroo.ai/v1/api/pipelines/infer/sample-pipeline-414/sample-pipeline - PATHS: The paths for each endpoint enabled. Endpoints differ depending on whether pipelines include models with OpenAI API compatibility enabled.
Retrieve Inference Endpoint API Spec Example
The following example demonstrates generating the the pipeline inference endpoint specification yaml format under the OpenAPI 3.1.1 format for the pipeline sample-pipeline.
Retrieve Token
There are two methods of retrieving the JWT token used to authenticate to the Wallaroo instance’s API service:
- Wallaroo SDK. This method requires a Wallaroo based user.
- API Client Secret. Allows any request with the secret client authentication credential to make an inference request.
This tutorial will use the Wallaroo SDK method for convenience with environmental variables for a seamless login without browser validation. For more information, see the Wallaroo SDK Essentials Guide: Client Connection.
API Request Methods
All Wallaroo API endpoints follow the format:
https://$WALLAROO_DOMAIN/v1/api$COMMAND
Where $COMMAND is the specific endpoint. For example, for the command to list of workspaces in the Wallaroo instance would use the above format based on these settings:
$WALLAROO_DOMAIN:wallaroo.example.com$COMMAND:/workspaces/list
This would create the following API endpoint:
https://wallaroo.example.com/v1/api/workspaces/list
Connect to Wallaroo and Authenticate via the Wallaroo SDK
For this example, a connection to the Wallaroo SDK is used. This will be used to retrieve the JWT token for the MLOps API calls.
This example will store the user’s credentials into the file ./creds.json which contains the following:
{
"username": "{Connecting User's Username}",
"password": "{Connecting User's Password}",
"email": "{Connecting User's Email Address}"
}
Replace the username, password, and email fields with the user account connecting to the Wallaroo instance. This allows a seamless connection to the Wallaroo instance and bypasses the standard browser based confirmation link. For more information, see the Wallaroo SDK Essentials Guide: Client Connection.
Update wallarooDomain variable to match the name of the Wallaroo Domain.
import wallaroo
from wallaroo.object import EntityNotFoundError
import pandas as pd
import os
import base64
import pyarrow as pa
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
# Used to create unique workspace and pipeline names
import string
import random
import json
# used to display dataframe information without truncating
from IPython.display import display
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)
# Retrieve the login credentials.
os.environ["WALLAROO_SDK_CREDENTIALS"] = './creds.json.example'
# wl = wallaroo.Client(auth_type="user_password")
# Client connection from local Wallaroo instance
wallarooDomain = 'wallaroo.example.com'
wl = wallaroo.Client(api_endpoint=f"https://{wallarooDOmain}",
auth_type="user_password")
wallarooDomain = "wallaroo.example.com"
APIURL=f"https://{wallarooDomain}/v1/api"
Retrieve the JWT Token
As mentioned earlier, there are multiple methods of authenticating to the Wallaroo instance for MLOps API calls. This tutorial will use the Wallaroo SDK method Wallaroo Client wl.auth.auth_header() method, extracting the token from the response.
Reference: MLOps API Retrieve Token Through Wallaroo SDK
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
display(headers)
{'Authorization': 'Bearer exampleabcdefg'}
Authenticate via API
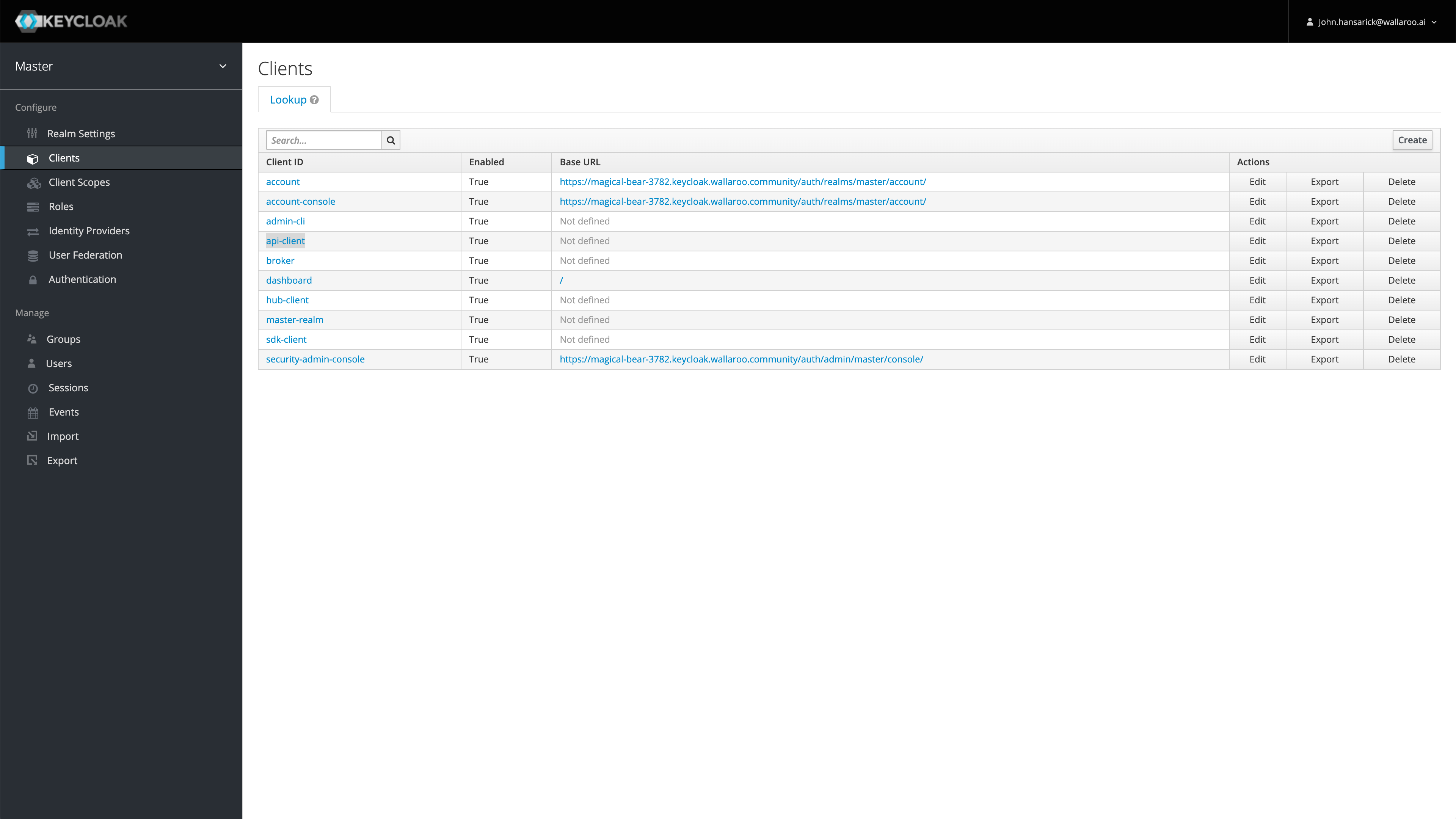
Wallaroo comes pre-installed with a confidential OpenID Connect client. The default client is api-client, but other clients may be created and configured.
Confidential clients require its secret to be supplied when requesting a token. Administrators may obtain their API client credentials from from the authentication URL /auth/admin/master/console/#/realms/master/clients.
For example, if the Wallaroo DNS address is https://wallaroo.example.com, then the direct path to the API client credentials is:
https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/admin/master/console/#/realms/master/clients
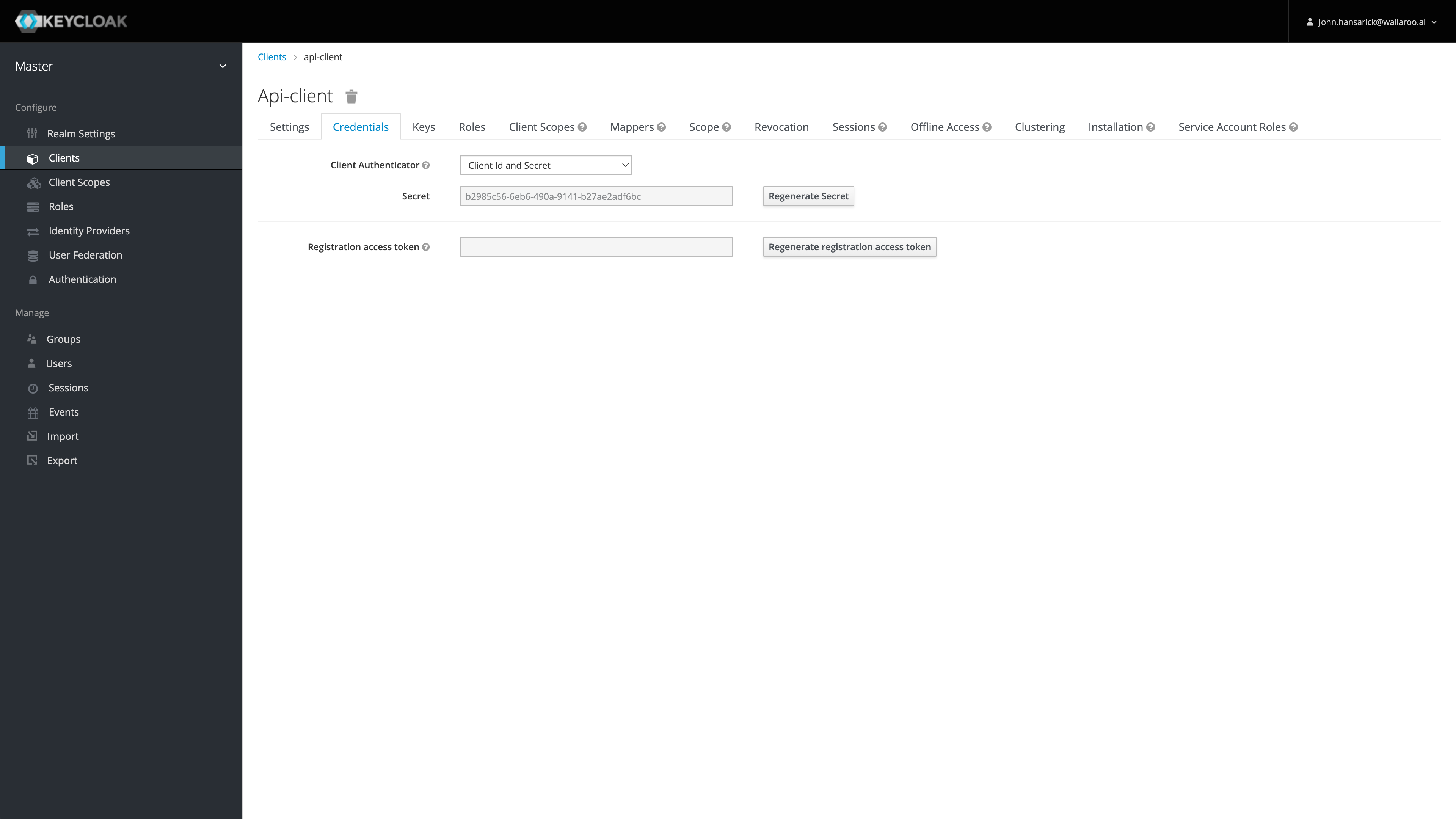
For this example, we are using the confidential client secret for api-client, which is found in the Wallaroo Authentication Service accessed by users with the role admin through the URL https://$WALLAROO_DOMAIN/auth. For more details, see How to Access the User Authentication Service. For this example, this is the secret for the user api-client. This is retrieved by:
- Access the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL.
- Select Administration Console.
- Logging in with a user with the role admin.
- Select Clients, then api-client.
- From the api-client page, select Credentials, then copy the client secret and store it in a safe location.
By default, tokens issued for api-client are valid for up to 60 minutes. Refresh tokens are supported.
There are two tokens used with Wallaroo API services:
- MLOps tokens: These tokens are used for making requests through the Wallaroo MLOps API, and require the authentication credentials (aka username and password) from the entity making the request. For more details, see the Wallaroo API Connection Guide.
- Inference Token: Tokens used as part of a Pipeline Inference URL request. These do not require a Wallaroo user credentials. Inference token requests require the following:
The Wallaroo instance authentication address.
The confidential client,
api-clientby default.The confidential client secret.
A
curlversion of that command is:TOKEN=$(curl "https://${WALLAROO_DOMAIN}/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token" -u "${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT}:${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET}" -d 'grant_type=client_credentials' -s | jq -r '.access_token')
The following examples demonstrates retrieving the inference token. The username and password for the user are stored in the file ./creds.json to prevent them from being displayed in a demonstration.
## Pipeline Inference URL token - does not require Wallaroo username/password.
TOKENURL=f'https://{WALLAROO_DOMAIN}/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
# Retrieving through os environmental variables
f = open('./creds.json')
login_data = json.load(f)
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT=login_data["confidentialClient"]
CLIENT_SECRET=login_data["confidentialPassword"]
auth = HTTPBasicAuth(CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT, CLIENT_SECRET)
data = {
'grant_type': 'client_credentials'
}
response = requests.post(TOKENURL, auth=auth, data=data, verify=True)
inference_access_token = response.json()['access_token']
display(inference_access_token)
'abc123'
Get External Inference URL
The API command /admin/get_pipeline_external_url retrieves the external inference URL for a specific pipeline in a workspace.
- Parameters
- workspace_id (REQUIRED integer): The workspace integer id.
- pipeline_name (REQUIRED string): The name of the pipeline.
In this example, a list of the workspaces will be retrieved. Based on the setup from the Internal Pipeline Deployment URL Tutorial, the workspace matching urlworkspace will have it’s workspace id stored and used for the /admin/get_pipeline_external_url request with the pipeline urlpipeline.
The External Inference URL is stored a variable for the next step.
Reference: Wallaroo MLOps API Essentials Guide: Pipeline Management: Get External Inference URL
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
# set Content-Type type
headers['Content-Type']='application/json'
## Retrieve the pipeline's External Inference URL
apiRequest = f"{APIURL}/v1/api/admin/get_pipeline_external_url"
data = {
"workspace_id": workspaceId,
"pipeline_name": pipeline_name
}
response = requests.post(apiRequest, json=data, headers=headers, verify=True).json()
deployurl = response['url']
deployurl
'https://api.autoscale-uat-ee.wallaroo.dev/v1/api/pipelines/infer/vsnaapiinferenceexamplepipeline-260/vsnaapiinferenceexamplepipeline'
Perform Inference via API
HTTP Headers
The following headers are required for connecting the the Pipeline Deployment URL:
Authorization: This requires the JWT token in the format
'Bearer ' + token. For example:Authorization: Bearer abcdefg==Content-Type:
For DataFrame formatted JSON:
Content-Type:application/json; format=pandas-recordsFor Arrow binary files, the
Content-Typeisapplication/vnd.apache.arrow.file.Content-Type:application/vnd.apache.arrow.file
Accept
Accept: application/json; format=pandas-records: The inference result is returned as a JSON in pandas Record format.Accept: application/vnd.apache.arrow.file: The inference result is returned as a binary in Apache Arrow format.
The inference can now be performed through the External Inference URL. This URL will accept the same inference data file that is used with the Wallaroo SDK, or with an Internal Inference URL as used in the Internal Pipeline Inference URL Tutorial.
For this example, the externalUrl retrieved through the Get External Inference URL is used to submit a single inference request through the data file data-1.json.
Reference: Wallaroo MLOps API Essentials Guide: Pipeline Management: Perform Inference Through External URL
Perform Inference via API Example: pandas Record
The following example demonstrates performing an inference using a pandas Record format input.
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
# set Content-Type type
headers['Content-Type']='application/json; format=pandas-records'
## Inference through external URL using dataframe
# retrieve the json data to submit
data = [
{
"tensor":[
1.0678324729,
0.2177810266,
-1.7115145262,
0.682285721,
1.0138553067,
-0.4335000013,
0.7395859437,
-0.2882839595,
-0.447262688,
0.5146124988,
0.3791316964,
0.5190619748,
-0.4904593222,
1.1656456469,
-0.9776307444,
-0.6322198963,
-0.6891477694,
0.1783317857,
0.1397992467,
-0.3554220649,
0.4394217877,
1.4588397512,
-0.3886829615,
0.4353492889,
1.7420053483,
-0.4434654615,
-0.1515747891,
-0.2668451725,
-1.4549617756
]
}
]
# submit the request via POST, import as pandas DataFrame
response = pd.DataFrame.from_records(
requests.post(
deployurl,
json=data,
headers=headers)
.json()
)
display(response.loc[:,["time", "out"]])
| time | out | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1688750664105 | {'dense_1': [0.0014974177]} |
Perform Inference via API Example: Apache Arrow
The following example demonstrates performing an inference using an Apache Arrow table as the input. The response is transformed into a pandas DataFrame for easier display.
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
# set Content-Type type
headers['Content-Type']='application/vnd.apache.arrow.file'
# set accept as apache arrow table
headers['Accept']="application/vnd.apache.arrow.file"
# Submit arrow file
dataFile="./data/cc_data_10k.arrow"
data = open(dataFile,'rb').read()
response = requests.post(
deployurl,
headers=headers,
data=data,
verify=True
)
# Arrow table is retrieved
with pa.ipc.open_file(response.content) as reader:
arrow_table = reader.read_all()
# convert to Polars DataFrame and display the first 5 rows
display(arrow_table.to_pandas().head(5).loc[:,["time", "out"]])
| time | out | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1688750664889 | {'dense_1': [0.99300325]} |
| 1 | 1688750664889 | {'dense_1': [0.99300325]} |
| 2 | 1688750664889 | {'dense_1': [0.99300325]} |
| 3 | 1688750664889 | {'dense_1': [0.99300325]} |
| 4 | 1688750664889 | {'dense_1': [0.0010916889]} |