Wallaroo API Connection Guide
Table of Contents
Wallaroo provides the MLOps API for changing a Wallaroo instance, such as adding workspaces, deploying pipelines, and other tasks. It also has the Pipeline Inference API for submitting inference requests to a deployed pipeline and receiving the results.
Token Types
There are two tokens used with Wallaroo API services: MLOps API tokens, and Inference Tokens.
| Token | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MLOps API Token |
| Used for MLOps API verification before accepting requests. the MLOps API token can be refreshed. |
| Pipeline Inference API Token | Either a MLOps API token, or an token returned from the confidential client and confidential secret submitted. Does not require a Wallaroo user. | Used to authenticate for inference requests through a deployed pipelines inference URL. |
How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret
Using the confidential client for token retrieval is only required for using the MLOps API to retrieve the MLOps API token.
Wallaroo comes pre-installed with a confidential OpenID Connect client. The default client is api-client, but other clients may be created and configured through the Wallaroo Authentication service.
The confidential client has a secret that is supplied during the token request. Administrators obtain their API client credentials from the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL http://{Wallaroo Domain}/auth/admin/master/console/#/realms/master/clients.
For example, if the Wallaroo Ops server is https://wallaroo.example.com, then the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL is:
https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/admin/master/console/#/realms/master/clients
See the Wallaroo DNS Guide for details on Wallaroo DNS integrations and URLs.
Administrators can access the Wallaroo Authentication Service dashboard from the url https://{Wallaroo Domain}/auth. For example, if the Wallaroo Domain is wallaroo.example.com, the Wallaroo Authentication Service dashboard url would be https://wallaroo.example.com/auth. For more details, see How to Access the User Authentication Service.
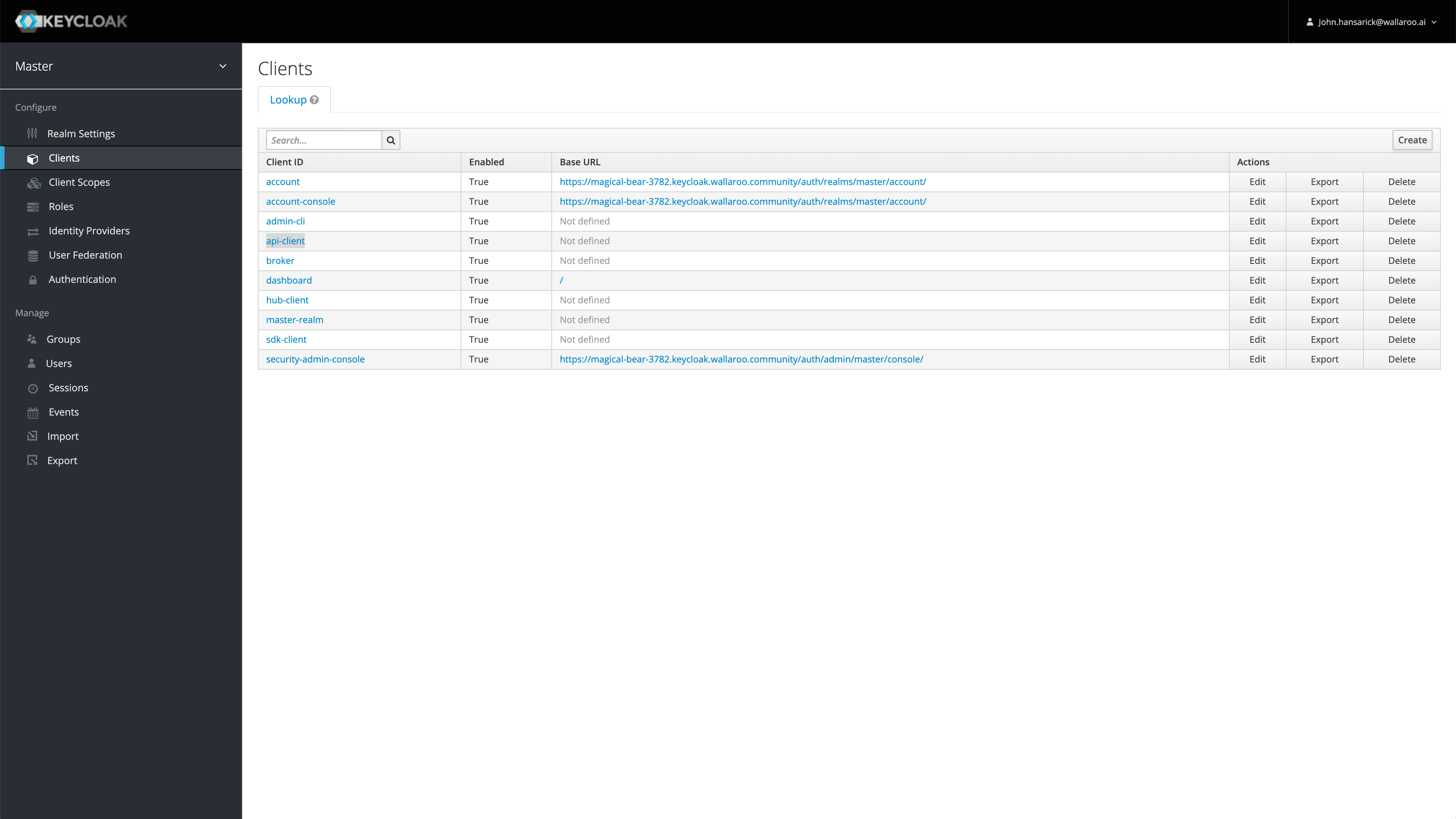
For this example, we are using the confidential client secret for the client api-client. For later examples, this is referred to as the CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT. The client secret for api-client is later referred to as the CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET. This is retrieved by:
- Access the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL.
- Select Administration Console.
- Logging in with a user with the role admin.
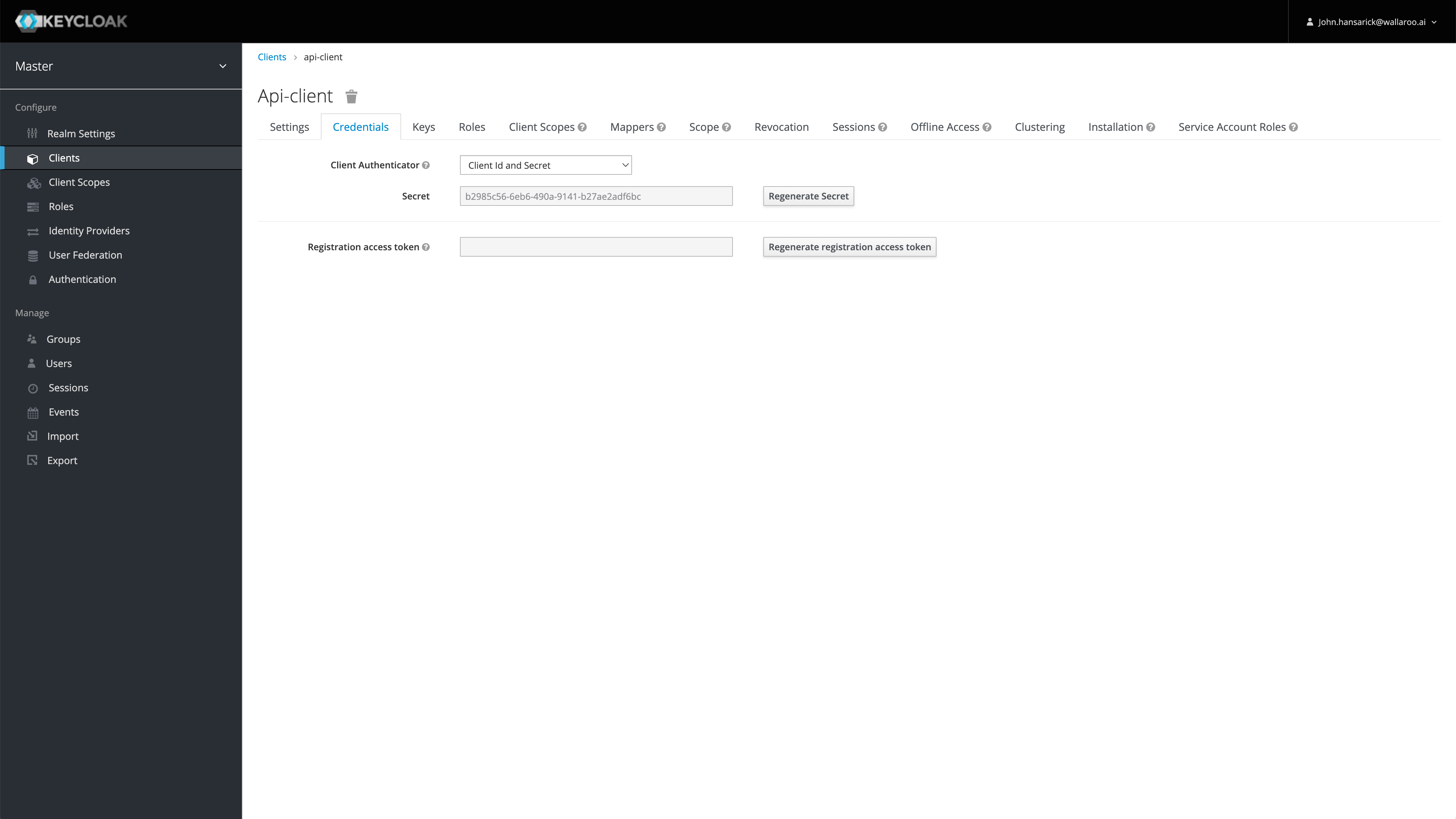
- Select Clients, then api-client, or create another client to use. This client name is used as the variable
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENTin the examples below. - From the api-client page, select Credentials, then copy the client secret and store it in a safe location. This is used as the variable
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRETin later examples.
By default, tokens issued for api-client are valid for up to 60 minutes. Refresh tokens are supported.
MLOps Token
MLOps API Tokens are generated either through an API request to the Wallaroo’s Authentication Service, or through the Wallaroo SDK.
Each API operation requires a valid JSON Web Token (JWT) obtained from Wallaroo’s Authentication Service.
For MLOps API Tokens, the JWT must include a valid Wallaroo user’s identity as Wallaroo access permissions are tied to specific platform users. For Pipeline Inference URL API requests, the token provided from the confidential client is sufficient.
To authenticate to the Wallaroo API, the options are either:
- Authenticate with the client secret via an API request
- Use the SDK command
Wallaroo.auth.auth_header()to retrieve the HTTP header including the token used to authenticate to the API.
MLOps Token through the API
- MLOps token: MLOps API Tokens are generated with the confidential client credentials and the username/password of the Wallaroo user making the MLOps API request and requires:
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service URL, which is the Wallaroo Domain and the suffix
/auth. For example, if the Wallaroo Domain iswallaroo.example.com, then the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL iswallaroo.example.com/auth. - The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client secret. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
- The Wallaroo username making the MLOps API request.
- The Wallaroo user’s password.
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service URL, which is the Wallaroo Domain and the suffix
This request return includes the access_token and the refresh_token. The access_token is used to authenticate. The refresh_token can be used to create a new token without submitting the original username and password.
- Tokens can be refreshed via a refresh request and require:
- The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client credentials. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
- The refresh token retrieved from the initial access token request.
- The confidential client,
MLOps Token through the SDK
Users connected to their Wallaroo instance via the Wallaroo SDK can use the Wallaroo.auth.auth_header() method to retrieve the appropriate header for their MLOps and Inference URL connection. The following shows making a connection to a Wallaroo instance, then retrieving the API header via the auth_header method.
MLOps Token Retrieval Examples
The following examples show how to retrieve the MLOps token through different means. MLOps tokens require the following:
- Via the Wallaroo Authentication Service service:
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service, which is the Wallaroo Domain with the suffix
/auth. For example, if the Wallaroo Domain iswallaroo.example.com, then the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL iswallaroo.example.com/auth. - The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client secret. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
- The Wallaroo username making the MLOps API request.
- The Wallaroo user’s password.
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service, which is the Wallaroo Domain with the suffix
- Via the Wallaroo SDK:
- The Wallaroo username making the MLOps API request.
- The Wallaroo user’s password.
For example, the following requests a token for the Wallaroo instance https://wallaroo.example.com for user mary.jane@example.com with the OpenID Connect Client api-client.
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
USERNAME = 'mary.jane@example.com'
PASSWORD = 'snugglebunnies'
eval $(curl "https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token" -u "${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT}:${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET}" -d "grant_type=password&username=${USERNAME}&password=${PASSWORD}&scope=offline_access' -s | jq -r '"TOKEN=\(.access_token) REFRESH=\(.refresh_token)"')
echo $TOKEN
abcdefg
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
USERNAME = 'mary.jane@example.com'
PASSWORD = 'snugglebunnies'
auth = HTTPBasicAuth(CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT, CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET)
data = {
'grant_type': 'password',
'username': USERNAME,
'password': PASSWORD
}
response = requests.post(TOKENURL, auth=auth, data=data, verify=True)
access_token = response.json()['access_token']
refresh_token = response.json()['refresh_token']
display(access_token)
abcdefg
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
display(headers)
{'Authorization': 'Bearer abcdefg'}
MLOps Token Refresh Examples
Tokens refreshment requires:
- Via the Keycloak API:
- The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client secret. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
- The refresh token retrieved from the initial access token request.
- The confidential client,
- Via the Wallaroo SDK:
- When using the Wallaroo SDK, the token is refreshed when
wl.auth.auth_header()is run.
- When using the Wallaroo SDK, the token is refreshed when
Note that for the refresh token, the Wallaroo user’s username and password are not required, but will require the refresh token retrieved during the initial access token retrieval process.
For example, the following requests a refresh token for the Wallaroo instance https://wallaroo.example.com for user mary.jane@example.com with the OpenID Connect Client api-client, with the refresh token already retrieved through the previous step.
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
TOKEN=$(curl "${TOKENURL}" -u "${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT}:${CLIENT_SECRET}" -d "grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=${REFRESH}" -s | jq -r '.access_token')
echo $TOKEN
abcdefg
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
auth = HTTPBasicAuth(CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT, CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET)
data = {
'grant_type': 'refresh_token',
'refresh_token': refresh_token
}
response = requests.post(TOKENURL, auth=auth, data=data, verify=True)
access_token = response.json()['access_token']
refresh_token = response.json()['refresh_token']
display(access_token)
abcdefg
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
display(headers)
{'Authorization': 'Bearer abcdefg'}
Request MLOps Operation with Token Example
With the token retrieved, a MLOps request can be performed.
The following examples shows how to make the request to retrieve a list of workspaces via the MLops API.
curl 'https://wallaroo.example.com/v1/api/workspaces/list' -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{}'
## Inference through external URL
apiRequest = "https://wallaroo.example.com/v1/api/workspaces/list"
# set the headers
headers= {
'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + TOKEN,
'Content-Type: application/json'
}
data = {
}
# submit the request via POST
response = requests.post(apiRequest, data=data, headers=headers)
Use the Wallaroo SDK to retrieve the MLOps token, then perform the List Workspaces MLOps API request with the Python Requests library.
# Retrieve the token through the Wallaroo SDK
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
apiRequest = "https://wallaroo.example.com/v1/api/workspaces/list"
data = {
}
response = requests.post(apiRequest, json=data, headers=headers, verify=True).json()
Inference Tokens
Inference Tokens through the API
- Inference Token: Tokens used as part of a Pipeline Inference URL request. These do not require a Wallaroo user credentials. Inference token request require the following:
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service URL.
- The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client secret. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
Retrieve Pipeline Inference URL Token
Inference Token: Tokens used as part of a Pipeline Inference URL request. These do not require a Wallaroo user credentials.
Note that MLOps API tokens can be used for Pipeline URL inference requests.
Inference token request require the following:
- Via the API:
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service URL, which is the Wallaroo Domain Name with the suffix
/auth. For example, if the Wallaroo Domain Name iswallaroo.example.com, then the Wallaroo Authentication Service URL iswallaroo.example.com/auth. - The confidential client,
api-clientby default. - The confidential client secret. See How to Retrieve the Confidential Client and Secret for details on retrieving the client secret.
- The Wallaroo Authentication Service URL, which is the Wallaroo Domain Name with the suffix
- Via the Wallaroo SDK
- The Wallaroo user’s username and password.
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
TOKEN=$(curl "${TOKENURL}" -u "${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT}:${CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT_SECRET}" -d 'grant_type=client_credentials' -s | jq -r '.access_token')
TOKENURL = 'https://wallaroo.example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token'
CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT ='api-client'
CLIENT_SECRET = 'abc123'
auth = HTTPBasicAuth(CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT, CLIENT_SECRET)
data = {
'grant_type': 'client_credentials'
}
response = requests.post(TOKENURL, auth=auth, data=data, verify=True)
inference_access_token = response.json()['access_token']
display(inference_access_token)
abcdefg
# Retrieve the token
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
display(headers)
{'Authorization': 'Bearer abcdefg'}
Perform Inference via Inference URL
The following demonstrates performing an inference request via a deployed pipeline’s inference URL, stored in the variable inference_url.
dataFile="./data/data_25k.arrow"
contentType="application/vnd.apache.arrow.file"
!curl -X POST $inference_url -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -H "Content-Type:$contentType" --data-binary @$dataFile > curl_response.df
headers = {
"Authorization": inference_access_token,
"Content-Type": 'application/json; format=pandas-records'
}
## Inference through external URL using dataframe
# retrieve the json data to submit
data = [
{
"tensor":[
1.0678324729,
0.2177810266,
-1.7115145262,
0.682285721,
1.0138553067,
-0.4335000013,
0.7395859437,
-0.2882839595,
-0.447262688,
0.5146124988,
0.3791316964,
0.5190619748,
-0.4904593222,
1.1656456469,
-0.9776307444,
-0.6322198963,
-0.6891477694,
0.1783317857,
0.1397992467,
-0.3554220649,
0.4394217877,
1.4588397512,
-0.3886829615,
0.4353492889,
1.7420053483,
-0.4434654615,
-0.1515747891,
-0.2668451725,
-1.4549617756
]
}
]
# submit the request via POST, import as pandas DataFrame
response = pd.DataFrame.from_records(
requests.post(
inference_url,
json=data,
headers=headers)
.json()
)
# Retrieve the token via the Wallaroo SDK
headers = wl.auth.auth_header()
# set Content-Type type
headers['Content-Type']='application/vnd.apache.arrow.file'
# set accept as apache arrow table
headers['Accept']="application/vnd.apache.arrow.file"
# Submit arrow file
dataFile="./data/cc_data_10k.arrow"
data = open(dataFile,'rb').read()
response = requests.post(
inference_url,
headers=headers,
data=data,
verify=True
)
# Arrow table is retrieved
with pa.ipc.open_file(response.content) as reader:
arrow_table = reader.read_all()