Wallaroo MLOps API Essentials Guide: Model Registry
Table of Contents
Wallaroo users can register their trained machine learning models from a model registry into their Wallaroo instance and perform inferences with it through a Wallaroo pipeline.
This guide details how to add ML Models from a model registry service into a Wallaroo instance.
Artifact Requirements
Models are uploaded to the Wallaroo instance as the specific artifact - the “file” or other data that represents the file itself. This must comply with the Wallaroo model requirements framework and version or it will not be deployed. Note that for models that fall outside of the supported model types, they can be registered to a Wallaroo workspace as MLFlow 1.30.0 containerized models.
Registry Services Roles
Registry service use in Wallaroo typically falls under the following roles.
| Role | Recommended Actions | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DevOps Engineer | Create Model Registry | Create the model (AKA artifact) registry service |
| Retrieve Model Registry Tokens | Generate the model registry service credentials. | |
| MLOps Engineer | Connect Model Registry to Wallaroo | Add the Registry Service URL and credentials into a Wallaroo instance for use by other users and scripts. |
| Add Wallaroo Registry Service to Workspace | Add the registry service configuration to a Wallaroo workspace for use by workspace users. | |
| Get Registry Details | Retrieve the connection details for a Wallaroo registry. | |
| Remove Wallaroo Registry from a Workspace | Add the registry service configuration to a Wallaroo workspace for use by workspace users. | |
| Data Scientist | List Models in Registry | List available models in a model registry. |
| List Model Version Artifacts | Retrieve the artifacts (usually files) for a model stored in a model registry. | |
| Upload Model from Registry | Upload a model and artifacts stored in a model registry into a Wallaroo workspace. |
Model Registry Operations
The following links to guides and information on setting up a model registry (also known as an artifact registry).
Create Model Registry
See Model serving with Azure Databricks for setting up a model registry service using Azure Databricks.
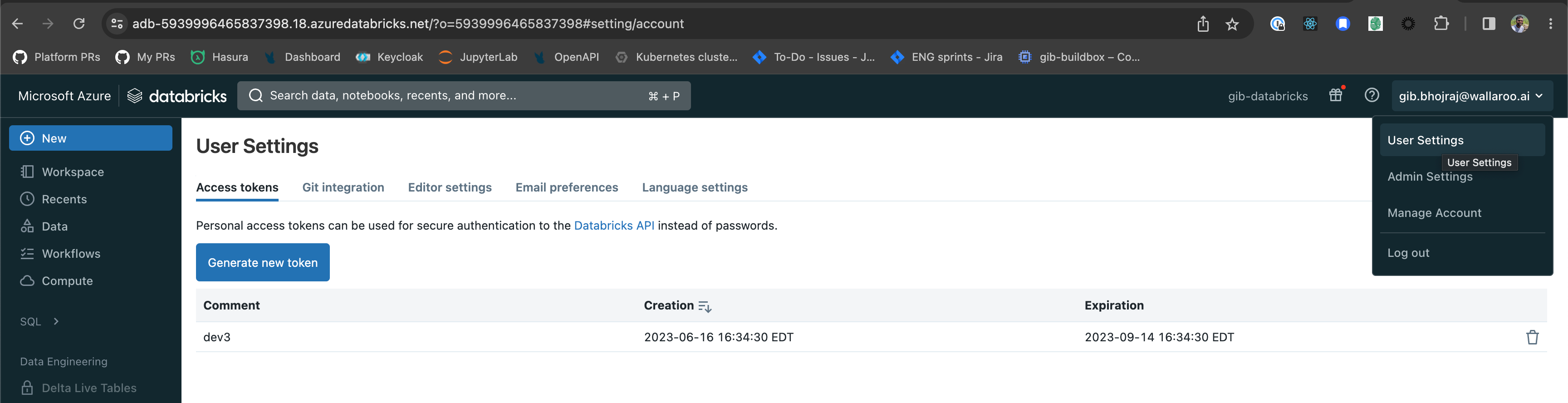
The following steps create an Access Token used to authenticate to an Azure Databricks Model Registry.
- Log into the Azure Databricks workspace.
- From the upper right corner access the User Settings.
- From the Access tokens, select Generate new token.
- Specify any token description and lifetime. Once complete, select Generate.
- Copy the token and store in a secure place. Once the Generate New Token module is closed, the token will not be retrievable.
The MLflow Model Registry provides a method of setting up a model registry service. Full details can be found at the MLflow Registry Guides.
A generic MLFlow model registry requires no token.
Wallaroo Registry Operations
- Connect Model Registry to Wallaroo: This details the link and connection information to a existing MLFlow registry service. Note that this does not create a MLFlow registry service, but adds the connection and credentials to Wallaroo to allow that MLFlow registry service to be used by other entities in the Wallaroo instance.
- Add a Registry to a Workspace: Add the created Wallaroo Model Registry so make it available to other workspace members.
- Remove a Registry from a Workspace: Remove the link between a Wallaroo Model Registry and a Wallaroo workspace.
Connect Model Registry to Wallaroo
MLFlow Registry connection information is added to a Wallaroo instance through the following endpoint.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models/create_registry
- PARAMETERS
- workspace_id (Integer Required): The numerical ID of the workspace to create the registry in.
- name (String Required): The name for the registry. Registry names are not unique.
- url (String Required): The full URL of the registry service. For example:
https://registry.wallaroo.ai - token (String Required): The authentication token used by the registry service.
- RETURNS
- id (String): The UUID of the registry.
- workspace_id: The numerical ID of the workspace the registry was connected to.
Connect Model Registry to Wallaroo Example
The following registry will be added to the workspace with the id 1.
import requests
token = "abcdefg"
x = requests.post("https://{APIURL}/v1/api/models/create_registry",
json={
"workspace_id": 1,
"name": "sample registry",
"url": "https://registry.wallaroo.ai",
"token": token
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
{'id': '98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29', 'workspace_id': 1}
Add Wallaroo Registry Service to Workspace
Registries are assigned to a Wallaroo workspace with the following endpoint. This allows members of the workspace to access the registry connection. A registry can be associated with one or more workspaces.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models//v1/api/models/attach_registry_to_workspace
- PARAMETERS
- workspace_id (Integer Required): The numerical ID of the workspace to create the registry in.
- registry_id (String Required): The ID of the registry in UUID format.
- RETURNS
- id (String): The UUID of the registry.
- workspace_id: The numerical ID of the workspace the registry was connected to.
Add Wallaroo Registry Service to Workspace Example
import requests
token = "abcdefg"
x = requests.post("https://{APIURL}/v1/api/models/attach_registry_to_workspace",
json={
'id': '98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29',
'workspace_id': 1},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
{
"registry_id": "3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
"workspace_id": 0
}
Remove Wallaroo Registry from a Workspace
Registries are removed from a registry with the following endpoint. This does not remove the registry connection information from the Wallaroo instance, merely removes the association between the registry and that particular workspace.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models//v1/api/models/remove_registry_from_workspace
- PARAMETERS
- workspace_id (Integer Required): The numerical ID of the workspace to remove the registry from.
- registry_id (String Required): The ID of the registry in UUID format.
- RETURNS
- id (String): The UUID of the registry.
- workspace_id: The numerical ID of the workspace the registry was connected to.
Remove Wallaroo Registry from a Workspace Example
import requests
token = "abcdefg"
x = requests.post("https://{APIURL}/v1/api/models/remove_registry_from_workspace",
json={
'id': '98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29',
'workspace_id': 1
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
{
"registry_id": "3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
"workspace_id": 0
}
Get Registry Details
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models/get_registry
- PARAMETERS
- id (String Required): The registry ID in UUID format.
- RETURNS
- id (String): The UUID of the registry.
- name (String Required): The name for the registry. Registry names are not unique.
- url (String Required): The full URL of the registry service. For example:
https://registry.wallaroo.ai - token (String Required): The authentication token used by the registry service.
- created_at (String Required): The creation date in DateTime format.
- updated_at (String Required): The updated date in DateTime format.
Get Registry Details Example
The following example demonstrates retrieving the registry with id 98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29.
import requests
x = requests.post("https://{APIURL}/v1/api/models/get_registry",
json={
"registry_id": '98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29'
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
{
'id': '98f9ca1d-c4e7-4d70-8df4-05c25a64be29',
'name': 'sample registry',
'url': 'https://registry.wallaroo.ai',
'token': 'dapi67c8c0b04606f730e78b7ae5e3221015-3',
'created_at': '2023-06-23T15:37:38.38427+00:00',
'updated_at': '2023-06-23T15:37:38.38427+00:00'
}
Wallaroo Registry Model Operations
List Registries in Workspace
A list of registries associates with a specific workspace are retrieved from the following endpoint.
- REQUEST URL
- POST
/v1/api/models/list_registries
- POST
- PARAMETERS
- workspace-id (String Required): The numerical id of the workspace.
- RETURNS
- A list of registries with the following fields.
- created_at (String): The UTC DateTime stamp of when the registry was created.
- id (String): The id of the Wallaroo registry in UUID format.
- name (String): The assigned name of the registry.
- token (String): The authentication token to the model registry.
- updated_at (String): The UTC DateTime stamp of when the registry was last updated.
- url (String): The URL to the registry service.
- A list of registries with the following fields.
List Registries in Workspace Example
import requests
x = requests.post("{APIURL}v1/api/models/list_registries",
json={
"workspace_id": 1
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
x.json()
[
{
"created_at": "2023-07-11T15:21:24.403Z",
"id": "3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
"name": "sample registry",
"token": "string",
"updated_at": "2023-07-11T15:21:24.403Z",
"url": "string"
}
]
List Models in a Registry
A List of models available to the Wallaroo instance through the MLFlow Registry is performed with the following endpoint.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models/list_registry_models
- PARAMETERS
- id (String Required): The registry ID in UUID format.
- RETURNS
- next_page_token (String): Used to retrieve the next List of models. If
None, there are no additional models to list after this request. - registered_models (List): List of Models based on the mlflow.entities.model_registry.ModelVersion specification.
- name (String): The name of the model.
- user_id (String): The ID of the user.
- latest_versions (List): The list of other versions of the model. If there are no other versions of the model, this will be
None. Each version has the following fields.- name (String): The name of the artifact.
- description (String): The description of the artifact.
- version (Integer): The version number. Other versions may be removed from the registry, so it is possible for a version to be higher than 1 even if there are no other versions still stored in the registry.
- status (String): The current status of the model.
- run_id (String): The run id from the MLFlow service that created the model.
- run_link (String): Link to the run from the MLFlow service that created the model.
- source (String): The URL for the specific version artifact on this registry service. For example:
'dbfs:/databricks/mlflow-tracking/123456/abcdefg/artifacts/random_forest_model'. - current_stage (String): The current stage of the model version.
- creation_timestamp (Integer): Creation timestamp in milliseconds since the Unix epoch.
- last_updated_timestamp (Integer): Last updated timestamp in milliseconds since the Unix epoch.
- next_page_token (String): Used to retrieve the next List of models. If
List Models in a Registry Example
import requests
x = requests.post("{APIURL}v1/api/models/list_registry_models",
json={
"registry_id": id
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
x.json()
{
'next_page_token': None,
'registered_models': [
{
'name': 'testmodel',
'user_id': 'sample.usersj@wallaroo.ai',
'latest_versions': None,
'creation_timestamp': 1686940722329,
'last_updated_timestamp': 1686940722329
},
{
'name': 'testmodel2',
'user_id': 'sample.user@wallaroo.ai',
'latest_versions': None,
'creation_timestamp': 1686940864528,
'last_updated_timestamp': 1686940864528
},
{
'name': 'wine_quality',
'user_id': 'sample.user@wallaroo.ai',
'latest_versions': [
{
'name': 'wine_quality',
'description': None,
'version': '1',
'status': 'READY',
'run_id': 'abcdefg',
'run_link': None,
'source': 'dbfs:/databricks/mlflow-tracking/abcdefg/abcdefg/artifacts/random_forest_model',
'current_stage': 'Archived',
'creation_timestamp': 1686942353367,
'last_updated_timestamp': 1686942597509
},
{
'name': 'wine_quality',
'description': None,
'version': '2',
'status': 'READY',
'run_id': 'abcdefg',
'run_link': None,
'source': 'dbfs:/databricks/mlflow-tracking/abcdefg/abcdefg/artifacts/model',
'current_stage': 'Production',
'creation_timestamp': 1686942576120,
'last_updated_timestamp': 1686942597646
}
],
'creation_timestamp': 1686942353127,
'last_updated_timestamp': 1686942597646
}
]
}
List Model Version Artifacts
The artifacts of a specific model version are retrieved through the following endpoint.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models/list_registry_model_version_artifacts
- PARAMETERS
- registry_id (String Required): The registry ID in UUID format.
- name (String Required): The name of the model to retrieve artifacts from.
- version (String Required): The version of the model to retrieve artifacts from.
- RETURNS
- List of artifacts with the following fields.
- file_size (Integer): The size of the file in bytes.
- full_path (String): The full path to the artifact. For example:
https://adb-5939996465837398.18.azuredatabricks.net/api/2.0/dbfs/read?path=/databricks/mlflow-registry/9f38797c1dbf4e7eb229c4011f0f1f18/models/testmodel2/model.pkl - is_dir (Boolean): Whether the artifact is a directory or file.
- modification_time (Integer): Last modification timestamp in milliseconds since the Unix epoch
- path (String): Relative path to the artifact within the registry. For example:
/databricks/mlflow-registry/9f38797c1dbf4e7eb229c4011f0f1f18/models/testmodel2/model.pkl
- List of artifacts with the following fields.
List Model Version Artifacts Example
import requests
x = requests.post("{APIURL}v1/api/models//list_registry_model_version_artifacts",
json={
"name": "wine_quality",
"registry_id": "3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
"version": "2"
},
headers=wl.auth.auth_header()
)
x.json()
[
{
"file_size": 156456,
"full_path": "https://adb-5939996465837398.18.azuredatabricks.net/api/2.0/dbfs/read?path=/databricks/mlflow-registry/9f38797c1dbf4e7eb229c4011f0f1f18/models/testmodel2/model.pkl",
"is_dir": false,
"modification_time": 1686942597646,
"path": "/databricks/mlflow-registry/9f38797c1dbf4e7eb229c4011f0f1f18/models/testmodel2/model.pkl"
}
]
Upload Model from Registry
Models are uploaded from a model registry configured in Wallaroo through the following endpoint. The specific artifact that is the model to be deployed is the item to upload to the Wallaroo workspace. Models must comply with Wallaroo model framework and versions as defined in Artifact Requirements.
- REQUEST URL
v1/api/models/upload_from_registry
- PARAMETERS
- registry_id (String Required): The registry ID in UUID format.
- name (String Required): The name to assign the model in Wallaroo. Model names map onto Kubernetes objects, and must be DNS compliant. The strings for model names must be lower case ASCII alpha-numeric characters or dash (-) only.
.and_are not allowed. - path (String Required): URL of the model to upload as specified in List Models in a Registry
sourcefield. - visibility (String Required): Whether the model is
publicorprivate. - workspace_id (Integer Required): The numerical id of the workspace to upload the model to.
- conversion (String Required): The conversion parameters that include the following:
- framework (String Required): The framework of the model being uploaded. See the list of supported models for more details.
- python_version (String Required): The version of Python required for model.
- requirements (String Required): Required libraries. Can be
[]if the requirements are default Wallaroo JupyterHub libraries. - input_schema (String Optional): The input schema from the Apache Arrow
pyarrow.lib.Schemaformat, encoded withbase64.b64encode. Only required for non-native runtime models. - output_schema (String Optional): The output schema from the Apache Arrow
pyarrow.lib.Schemaformat, encoded withbase64.b64encode. Only required for non-native runtime models.
- RETURNS
- model_id (String): The numerical id of the model uploaded
Upload Model from Registry Example
import requests
x = requests.post("{APIURL}v1/api/models/upload_from_registry", json={
"registry_id": id,
"name": "uploaded-model-name",
"path": "<DBFS URL from list_artifacts() call here>",
"visibility": "public",
"workspace_id": 1,
"conversion": {
"framework": "sklearn",
"requirements": [],
},
"input_schema": "<base64-encoded input schema here>",
"output_schema": "<base64-encoded output schema here>"
}, headers=wl.auth.auth_header())
x.json()
{'model_id': 34}