Model Observability with Assays
Features:
Models:
This tutorial and the assets can be downloaded as part of the Wallaroo Tutorials repository.
Model Drift Observability with Assays
The Model Insights feature lets you monitor how the environment that your model operates within may be changing in ways that affect it’s predictions so that you can intervene (retrain) in an efficient and timely manner. Changes in the inputs, data drift, can occur due to errors in the data processing pipeline or due to changes in the environment such as user preference or behavior.
This notebook focuses on interactive exploration over historical data. After you are comfortable with how your data has behaved historically, you can schedule this same analysis (called an assay) to automatically run periodically, looking for indications of data drift or concept drift.
In this notebook, we will be running a drift assay on an ONNX model pre-trained to predict house prices.
Goal
Model insights monitors the output of the spam classifier model over a designated time window and compares it to an expected baseline distribution. We measure the difference between the window distribution and the baseline distribution; large differences indicate that the behavior of the model (or its inputs) has changed from what we expect. This possibly indicates a change that should be accounted for, possibly by retraining the models.
Resources
This tutorial provides the following:
- Models:
models/rf_model.onnx: The champion model that has been used in this environment for some time.- Various inputs:
smallinputs.df.json: A set of house inputs that tends to generate low house price values.biginputs.df.json: A set of house inputs that tends to generate high house price values.
Prerequisites
- A deployed Wallaroo instance
- The following Python libraries installed:
Steps
- Deploying a sample ML model used to determine house prices based on a set of input parameters.
- Build an assay baseline from a set of baseline start and end dates, and an assay baseline from a numpy array.
- Preview the assay and show different assay configurations.
- Upload the assay.
- View assay results.
- Pause and resume the assay.
Import Libraries
The first step will be to import our libraries, and set variables used through this tutorial.
import wallaroo
from wallaroo.object import EntityNotFoundError
from wallaroo.framework import Framework
from IPython.display import display
# used to display DataFrame information without truncating
from IPython.display import display
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)
import datetime
import time
workspace_name = f'assay-demonstration-tutorial-2'
main_pipeline_name = f'assay-demonstration-tutorial'
model_name_control = f'house-price-estimator'
model_file_name_control = './models/rf_model.onnx'
# Set the name of the assay
assay_name=f"house price assay demo"
# ignoring warnings for demonstration
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# used to display DataFrame information without truncating
from IPython.display import display
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)
Connect to the Wallaroo Instance
The first step is to connect to Wallaroo through the Wallaroo client. The Python library is included in the Wallaroo install and available through the Jupyter Hub interface provided with your Wallaroo environment.
This is accomplished using the wallaroo.Client() command, which provides a URL to grant the SDK permission to your specific Wallaroo environment. When displayed, enter the URL into a browser and confirm permissions. Store the connection into a variable that can be referenced later.
If logging into the Wallaroo instance through the internal JupyterHub service, use wl = wallaroo.Client(). For more information on Wallaroo Client settings, see the Client Connection guide.
# Login through local Wallaroo instance
wl = wallaroo.Client()
Create Workspace
We will create a workspace to manage our pipeline and models. The following variables will set the name of our sample workspace then set it as the current workspace.
Workspace, pipeline, and model names should be unique to each user, so we’ll add in a randomly generated suffix so multiple people can run this tutorial in a Wallaroo instance without effecting each other.
workspace = wl.get_workspace(name=workspace_name, create_if_not_exist=True)
wl.set_current_workspace(workspace)
{'name': 'assay-demonstration-tutorial-2', 'id': 29, 'archived': False, 'created_by': '13486fc4-a1a7-43e2-9233-62177d5f739b', 'created_at': '2024-07-16T17:12:14.37779+00:00', 'models': [], 'pipelines': []}
Upload The Champion Model
For our example, we will upload the champion model that has been trained to derive house prices from a variety of inputs. The model file is rf_model.onnx, and is uploaded with the name house-price-estimator.
housing_model_control = (wl.upload_model(model_name_control,
model_file_name_control,
framework=Framework.ONNX)
.configure(tensor_fields=["tensor"])
)
Build the Pipeline
This pipeline is made to be an example of an existing situation where a model is deployed and being used for inferences in a production environment. We’ll call it assay-demonstration-tutorial, set housing_model_control as a pipeline step, then run a few sample inferences.
This pipeline will be a simple one - just a single pipeline step.
mainpipeline = wl.build_pipeline(main_pipeline_name)
# clear the steps if used before
mainpipeline.clear()
mainpipeline.add_model_step(housing_model_control)
#minimum deployment config
deploy_config = wallaroo.DeploymentConfigBuilder().replica_count(1).cpus(0.5).memory("1Gi").build()
mainpipeline.deploy(deployment_config = deploy_config)
Waiting for deployment - this will take up to 45s ........... ok
| name | assay-demonstration-tutorial |
|---|---|
| created | 2024-07-16 17:12:15.096674+00:00 |
| last_updated | 2024-07-16 17:12:15.152669+00:00 |
| deployed | True |
| workspace_id | 29 |
| workspace_name | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 |
| arch | x86 |
| accel | none |
| tags | |
| versions | 3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa, 5fcb820c-671b-48fc-b7ee-869e72fce4e5 |
| steps | house-price-estimator |
| published | False |
Testing
We’ll use two inferences as a quick sample test - one that has a house that should be determined around $700k, the other with a house determined to be around $1.5 million.
normal_input = pd.DataFrame.from_records({"tensor": [[4.0, 2.5, 2900.0, 5505.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.0, 8.0, 2900.0, 0.0, 47.6063, -122.02, 2970.0, 5251.0, 12.0, 0.0, 0.0]]})
result = mainpipeline.infer(normal_input)
display(result)
| time | in.tensor | out.variable | anomaly.count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2024-07-16 17:12:27.056 | [4.0, 2.5, 2900.0, 5505.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 3.0, 8.0, 2900.0, 0.0, 47.6063, -122.02, 2970.0, 5251.0, 12.0, 0.0, 0.0] | [718013.7] | 0 |
large_house_input = pd.DataFrame.from_records({'tensor': [[4.0, 3.0, 3710.0, 20000.0, 2.0, 0.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 2760.0, 950.0, 47.6696, -122.261, 3970.0, 20000.0, 79.0, 0.0, 0.0]]})
large_house_result = mainpipeline.infer(large_house_input)
display(large_house_result)
| time | in.tensor | out.variable | anomaly.count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2024-07-16 17:12:27.099 | [4.0, 3.0, 3710.0, 20000.0, 2.0, 0.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 2760.0, 950.0, 47.6696, -122.261, 3970.0, 20000.0, 79.0, 0.0, 0.0] | [1514079.4] | 0 |
Generate Sample Data
Before creating the assays, we must generate data for the assays to build from.
For this example, we will:
- Perform sample inferences based on lower priced houses and use that as our baseline.
- Generate inferences from specific set of high priced houses create inference outputs that will be outside the baseline. This is used in later steps to demonstrate baseline comparison against assay analyses.
Inference Results History Generation
To start the demonstration, we’ll create a set of inferences based on houses with small estimated prices.
We will save the beginning and end periods of inferences to the variables assay_baseline_start and assay_baseline_end. These will be used later to create assay baselines from a range of dates.
small_houses_inputs = pd.read_json('./data/smallinputs.df.json')
baseline_size = 500
# Where the baseline data will start
assay_baseline_start = datetime.datetime.now()
# These inputs will be random samples of small priced houses. Around 30,000 is a good number
small_houses = small_houses_inputs.sample(baseline_size, replace=True).reset_index(drop=True)
# Wait 60 seconds to set this data apart from the rest
time.sleep(60)
small_results = mainpipeline.infer(small_houses)
# Set the baseline end
assay_baseline_end = datetime.datetime.now()
Generate Numpy Baseline Values
From our inference outputs, we will create an array of numpy values. These are used for assays baselines created from numpy values.
# get the numpy values
# set the results to a non-array value
small_results_baseline_df = small_results.copy()
small_results_baseline_df['variable']=small_results['out.variable'].map(lambda x: x[0])
small_results_baseline_df
# set the numpy array
small_results_baseline = small_results_baseline_df['variable'].to_numpy()
Assay Test Data
The following will generate inference data for us to test against the assay baseline. For this, we will add in house data that generate higher house prices than the baseline data we used earlier.
This process should take 6 minutes to generate the historical data we’ll later use in our assays. We store the DateTime assay_window_start to determine where to start out assay analyses.
# Get a spread of house values
# # Set the start for our assay window period.
assay_window_start = datetime.datetime.now()
time.sleep(65)
inference_size = 1000
# And a spread of large house values
small_houses_inputs = pd.read_json('./data/smallinputs.df.json', orient="records")
small_houses = small_houses_inputs.sample(inference_size, replace=True).reset_index(drop=True)
mainpipeline.infer(small_houses)
time.sleep(65)
# Get a spread of large house values
time.sleep(65)
inference_size = 1000
# And a spread of large house values
big_houses_inputs = pd.read_json('./data/biginputs.df.json', orient="records")
big_houses = big_houses_inputs.sample(inference_size, replace=True).reset_index(drop=True)
mainpipeline.infer(big_houses)
time.sleep(65)
Model Insights via the Wallaroo Dashboard SDK
Assays generated through the Wallaroo SDK can be previewed, configured, and uploaded to the Wallaroo Ops instance. The following is a condensed version of this process. For full details see the Wallaroo SDK Essentials Guide: Assays Management guide.
Model drift detection with assays using the Wallaroo SDK follows this general process.
- Define the Baseline: From either historical inference data for a specific model in a pipeline, or from a pre-determine array of data, a baseline is formed.
- Assay Preview: Once the baseline is formed, we preview the assay and configure the different options until we have the the best method of detecting environment or model drift.
- Create Assay: With the previews and configuration complete, we upload the assay. The assay will perform an analysis on a regular scheduled based on the configuration.
- Get Assay Results: Retrieve the analyses and use them to detect model drift and possible sources.
- Pause/Resume Assay: Pause or restart an assay as needed.
Define the Baseline
Assay baselines are defined with the wallaroo.client.build_assay method. Through this process we define the baseline from either a range of dates or pre-generated values.
wallaroo.client.build_assay take the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assay_name | String (Required) - required | The name of the assay. Assay names must be unique across the Wallaroo instance. |
| pipeline | wallaroo.pipeline.Pipeline (Required) | The pipeline the assay is monitoring. |
| model_name | String (Optional) / None | The name of the model to monitor. This field should only be used to track the inputs/outputs for a specific model step in a pipeline. If no model_name is to be included, then the parameters must be passed a named parameters not positional ones. |
| iopath | String (Required) | The input/output data for the model being tracked in the format input/output field index. Only one value is tracked for any assay. For example, to track the output of the model’s field house_value at index 0, the iopath is 'output house_value 0. |
| baseline_start | datetime.datetime (Optional) | The start time for the inferences to use as the baseline. Must be included with baseline_end. Cannot be included with baseline_data. |
| baseline_end | datetime.datetime (Optional) | The end time of the baseline window. the baseline. Windows start immediately after the baseline window and are run at regular intervals continuously until the assay is deactivated or deleted. Must be included with baseline_start. Cannot be included with baseline_data.. |
| baseline_data | numpy.array (Optional) | The baseline data in numpy array format. Cannot be included with either baseline_start or baseline_data. |
Note that model_name is an optional parameters when parameters are named. For example:
assay_builder_from_dates = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
or:
assay_builder_from_dates = wl.build_assay("assays from date baseline",
mainpipeline,
None, ## since we are using positional parameters, `None` must be included for the model parameter
"output variable 0",
assay_baseline_start,
assay_baseline_end)
Baselines are created in one of two mutually exclusive methods:
- Date Range: The
baseline_startandbaseline_endretrieves the inference requests and results for the pipeline from the start and end period. This data is summarized and used to create the baseline. For our examples, we’re using the variablesassay_baseline_startandassay_baseline_endto represent a range of dates, withassay_baseline_startbeing set beforeassay_baseline_end. - Numpy Values: The
baseline_datasets the baseline from a provided numpy array. This allows assay baselines to be created without first performing inferences in Wallaroo.
Define the Baseline Example
This example shows two methods of defining the baseline for an assay:
"assays from date baseline": This assay uses historical inference requests to define the baseline. This assay is saved to the variableassay_builder_from_dates."assays from numpy": This assay uses a pre-generated numpy array to define the baseline. This assay is saved to the variableassay_builder_from_numpy.
In both cases, the following parameters are used:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| assay_name | "assays from date baseline" and "assays from numpy" |
| pipeline | mainpipeline: A pipeline with a ML model that predicts house prices. The output field for this model is variable. |
| iopath | These assays monitor the model’s output field variable at index 0 for the pipeline. From this, the iopath setting is "output variable 0". |
The difference between the two assays’ parameters determines how the baseline is generated.
"assays from date baseline": Uses thebaseline_startandbaseline_endto set the time period of inference requests and results to gather data from."assays from numpy": Uses a pre-generated numpy array as for the baseline data.
First we generate an assay baseline from a range of historical inferences performed through the specified pipeline deployment.
# Build the assay, based on the start and end of our baseline time,
# and tracking the output variable index 0
display(assay_baseline_start)
display(assay_baseline_end)
assay_baseline_from_dates = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# create the baseline from the dates
assay_baseline_run_from_dates = assay_baseline_from_dates.build().interactive_baseline_run()
datetime.datetime(2024, 7, 16, 17, 12, 27, 123262)
datetime.datetime(2024, 7, 16, 17, 13, 27, 222295)
In this code sample, we generate the assay baseline from a preset numpy array called small_results_baseline.
# build the baseline from the numpy array
display(small_results_baseline[0:5])
# assay builder by baseline
assay_baseline_from_numpy = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from numpy",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_data = small_results_baseline)
# create the baseline from the numpy array
assay_baseline_run_from_numpy = assay_baseline_from_numpy.build().interactive_baseline_run()
array([ 318011.4 , 383833.88, 1295531.8 , 437177.97, 513264.66])
Baseline Chart
The baseline chart is displayed with wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysis.chart(), which returns a chart with:
- baseline mean: The mean value of the baseline values.
- baseline median: The median value of the baseline values.
- bin_mode: The binning mode. See Binning Mode
- aggregation: The aggregation type. See Aggregation Options
- metric: The assay’s metric type. See Score Metric
- weighted: Whether the binning mode is weighted. See Binning Mode
The first chart is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_run_from_dates.chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
baseline median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False

This chart is from an assay baseline generated from a set of numpy values.
assay_baseline_run_from_numpy.chart()
baseline mean = 513781.2065599997
baseline median = 448627.8
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False

Baseline DataFrame
The method wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.baseline_dataframe returns a DataFrame of the assay baseline generated from the provided parameters. This includes:
metadata: The inference metadata with the model information, inference time, and other related factors.indata: Each input field assigned with the labelin.{input field name}.outdata: Each output field assigned with the labelout.{output field name}
Note that for assays generated from numpy values, there is only the out data based on the supplied baseline data.
In the following example, the baseline DataFrame is retrieved.
This baseline DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
display(assay_baseline_from_dates.baseline_dataframe())
| time | metadata | input_tensor_0 | input_tensor_1 | input_tensor_2 | input_tensor_3 | input_tensor_4 | input_tensor_5 | input_tensor_6 | input_tensor_7 | ... | input_tensor_9 | input_tensor_10 | input_tensor_11 | input_tensor_12 | input_tensor_13 | input_tensor_14 | input_tensor_15 | input_tensor_16 | input_tensor_17 | output_variable_0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 3.0 | 2.00 | 1590.0 | 87120.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ... | 1590.0 | 0.0 | 47.224098 | -122.071999 | 2780.0 | 183161.0 | 16.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.180114e+05 |
| 1 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 4.0 | 2.50 | 3200.0 | 6691.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | ... | 3200.0 | 0.0 | 47.367001 | -122.030998 | 2610.0 | 6510.0 | 13.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.838339e+05 |
| 2 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 4.0 | 3.25 | 5180.0 | 19850.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ... | 3540.0 | 1640.0 | 47.562000 | -122.162003 | 3160.0 | 9750.0 | 9.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.295532e+06 |
| 3 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 3.0 | 2.00 | 1790.0 | 6800.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | ... | 1240.0 | 550.0 | 47.728001 | -122.338997 | 1470.0 | 6800.0 | 51.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.371780e+05 |
| 4 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 3.0 | 1.75 | 2220.0 | 11646.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | ... | 1270.0 | 950.0 | 47.776199 | -122.269997 | 1490.0 | 10003.0 | 64.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.132647e+05 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 495 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 3.0 | 2.50 | 2160.0 | 8809.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | ... | 1540.0 | 620.0 | 47.699402 | -122.348999 | 930.0 | 5420.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7.261818e+05 |
| 496 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 2.0 | 2.50 | 1785.0 | 779.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | ... | 1595.0 | 190.0 | 47.595901 | -122.197998 | 1780.0 | 794.0 | 39.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.596311e+05 |
| 497 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 4.0 | 2.50 | 1750.0 | 6397.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | ... | 1750.0 | 0.0 | 47.308201 | -122.358002 | 1940.0 | 6502.0 | 27.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.912398e+05 |
| 498 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 4.0 | 2.25 | 2130.0 | 8499.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | ... | 1600.0 | 530.0 | 47.365700 | -122.209999 | 1890.0 | 11368.0 | 39.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.342577e+05 |
| 499 | 1721150007209 | {'last_model': '{"model_name":"house-price-estimator","model_sha":"e22a0831aafd9917f3cc87a15ed267797f80e2afa12ad7d8810ca58f173b8cc6"}', 'pipeline_version': '3307faae-8a2f-4079-866b-f474d99f55aa', 'elapsed': [2159729, 3663809], 'dropped': [], 'partition': 'engine-5cfd766455-k42dw'} | 2.0 | 2.25 | 1660.0 | 2128.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | ... | 1660.0 | 0.0 | 47.752800 | -122.251999 | 1640.0 | 2128.0 | 41.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.371780e+05 |
500 rows × 21 columns
This baseline DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from an array of numpy values.
display(assay_baseline_from_numpy.baseline_dataframe())
| output_variable_0 | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 318011.40 |
| 1 | 383833.88 |
| 2 | 1295531.80 |
| 3 | 437177.97 |
| 4 | 513264.66 |
| ... | ... |
| 495 | 726181.75 |
| 496 | 559631.06 |
| 497 | 291239.75 |
| 498 | 334257.70 |
| 499 | 437177.97 |
500 rows × 1 columns
Baseline Stats
The method wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysis.baseline_stats() returns a pandas.core.frame.DataFrame of the baseline stats.
The baseline stats for each assay are displayed in the examples below.
This baseline states DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_run_from_dates.baseline_stats()
| Baseline | |
|---|---|
| count | 500 |
| min | 236238.671875 |
| max | 1295531.75 |
| mean | 513781.205375 |
| median | 448627.8125 |
| std | 233066.759431 |
| start | 2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00 |
| end | 2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 |
This baseline states DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from an array of numpy values.
assay_baseline_run_from_numpy.baseline_stats()
| Baseline | |
|---|---|
| count | 500 |
| min | 236238.67 |
| max | 1295531.8 |
| mean | 513781.20656 |
| median | 448627.8 |
| std | 233066.761363 |
| start | None |
| end | None |
Baseline Bins
The method wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysis.baseline_bins a simple dataframe to with the edge/bin data for a baseline.
These baseline bins DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_run_from_dates.baseline_bins()
| b_edges | b_edge_names | b_aggregated_values | b_aggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.362387e+05 | left_outlier | 0.0 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 1 | 3.109929e+05 | q_20 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 2 | 4.319922e+05 | q_40 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 3 | 4.759715e+05 | q_60 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 4 | 7.019407e+05 | q_80 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 5 | 1.295532e+06 | q_100 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 6 | inf | right_outlier | 0.0 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
These baseline bins DataFrame is from an assay baseline generated from an array of numpy values.
assay_baseline_run_from_numpy.baseline_bins()
| b_edges | b_edge_names | b_aggregated_values | b_aggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 236238.67 | left_outlier | 0.0 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 1 | 310992.94 | q_20 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 2 | 431992.22 | q_40 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 3 | 475971.50 | q_60 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 4 | 701940.70 | q_80 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 5 | 1295531.80 | q_100 | 0.2 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
| 6 | inf | right_outlier | 0.0 | Aggregation.DENSITY |
Baseline Histogram Chart
The method wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.baseline_histogram returns a histogram chart of the assay baseline generated from the provided parameters.
These chart is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_from_dates.baseline_histogram()

Baseline KDE Chart
The method wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.baseline_kde returns a Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) chart of the assay baseline generated from the provided parameters.
These chart is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_from_dates.baseline_kde()

Baseline ECDF Chart
The method wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.baseline_ecdf returns a Empirical Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) chart of the assay baseline generated from the provided parameters.
These chart is from an assay baseline generated from a set of inferences across a range of dates.
assay_baseline_from_dates.baseline_ecdf()

Assay Preview
Now that the baseline is defined, we look at different configuration options and view how the assay baseline and results changes. Once we determine what gives us the best method of determining model drift, we can create the assay.
Analysis List Chart Scores
Analysis List scores show the assay scores for each assay result interval in one chart. Values that are outside of the alert threshold are colored red, while scores within the alert threshold are green.
Assay chart scores are displayed with the method wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysisList.chart_scores(title: Optional[str] = None), with ability to display an optional title with the chart.
The following example shows retrieving the assay results and displaying the chart scores. From our example, we have two windows - the first should be green, and the second is red showing that values were outside the alert threshold.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# Preview the assay analyses
assay_results.chart_scores()

Analysis Chart
The method wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysis.chart() displays a comparison between the baseline and an interval of inference data.
This is compared to the Chart Scores, which is a list of all of the inference data split into intervals, while the Analysis Chart shows the breakdown of one set of inference data against the baseline.
Score from the Analysis List Chart Scores and each element from the Analysis List DataFrame generates
The following fields are included.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| baseline mean | Float | The mean of the baseline values. |
| window mean | Float | The mean of the window values. |
| baseline median | Float | The median of the baseline values. |
| window median | Float | The median of the window values. |
| bin_mode | String | The binning mode used for the assay. |
| aggregation | String | The aggregation mode used for the assay. |
| metric | String | The metric mode used for the assay. |
| weighted | Bool | Whether the bins were manually weighted. |
| score | Float | The score from the assay window. |
| scores | List(Float) | The score from each assay window bin. |
| index | Integer/None | The window index. Interactive assay runs are None. |
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display one of the analysis from the total results
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.008604680420075936
scores = [0.0, 0.001015989699687698, 0.0009472210786334042, 0.0033382848156130714, 0.002503651312977887, 0.0001265890399214496, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

Analysis List DataFrame
wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysisList.to_dataframe() returns a DataFrame showing the assay results for each window aka individual analysis. This DataFrame contains the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assay_id | Integer/None | The assay id. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| name | String/None | The name of the assay. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| iopath | String/None | The iopath of the assay. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| score | Float | The assay score. |
| start | DateTime | The DateTime start of the assay window. |
| min | Float | The minimum value in the assay window. |
| max | Float | The maximum value in the assay window. |
| mean | Float | The mean value in the assay window. |
| median | Float | The median value in the assay window. |
| std | Float | The standard deviation value in the assay window. |
| warning_threshold | Float/None | The warning threshold of the assay window. |
| alert_threshold | Float/None | The alert threshold of the assay window. |
| status | String | The assay window status. Values are:
|
For this example, the assay analysis list DataFrame is listed.
From this tutorial, we should have 2 windows of dta to look at, each one minute apart. The first window should show status: OK, with the second window with the very large house prices will show status: alert
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display the dataframe from the analyses
assay_results.to_dataframe()
| id | assay_id | assay_name | iopath | pipeline_id | pipeline_name | workspace_id | workspace_name | score | start | min | max | mean | median | std | warning_threshold | alert_threshold | status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | None | assays from date baseline | None | None | None | 0.008605 | 2024-07-16T17:14:27.239563+00:00 | 2.362387e+05 | 1489624.250 | 5.127795e+05 | 4.486278e+05 | 226255.370366 | None | 0.25 | Ok | ||
| 1 | None | None | assays from date baseline | None | None | None | 8.868483 | 2024-07-16T17:16:27.239563+00:00 | 1.514079e+06 | 2016006.125 | 1.881163e+06 | 1.946438e+06 | 162405.590663 | None | 0.25 | Alert |
Analysis List Full DataFrame
wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysisList.to_full_dataframe() returns a DataFrame showing all values, including the inputs and outputs from the assay results for each window aka individual analysis. This DataFrame contains the following fields:
pipeline_id warning_threshold bin_index created_at
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| window_start | DateTime | The date and time when the window period began. |
| analyzed_at | DateTime | The date and time when the assay analysis was performed. |
| elapsed_millis | Integer | How long the analysis took to perform in milliseconds. |
| baseline_summary_count | Integer | The number of data elements from the baseline. |
| baseline_summary_min | Float | The minimum value from the baseline summary. |
| baseline_summary_max | Float | The maximum value from the baseline summary. |
| baseline_summary_mean | Float | The mean value of the baseline summary. |
| baseline_summary_median | Float | The median value of the baseline summary. |
| baseline_summary_std | Float | The standard deviation value of the baseline summary. |
| baseline_summary_edges_{0…n} | Float | The baseline summary edges for each baseline edge from 0 to number of edges. |
| summarizer_type | String | The type of summarizer used for the baseline. See wallaroo.assay_config for other summarizer types. |
| summarizer_bin_weights | List / None | If baseline bin weights were provided, the list of those weights. Otherwise, None. |
| summarizer_provided_edges | List / None | If baseline bin edges were provided, the list of those edges. Otherwise, None. |
| status | String | The assay window status. Values are:
|
| id | Integer/None | The id for the window aka analysis. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| assay_id | Integer/None | The assay id. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| pipeline_id | Integer/None | The pipeline id. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
| warning_threshold | Float | The warning threshold set for the assay. |
| warning_threshold | Float | The warning threshold set for the assay. |
| bin_index | Integer/None | The bin index for the window aka analysis. |
| created_at | Datetime/None | The date and time the window aka analysis was generated. Only provided from uploaded and executed assays. |
For this example, full DataFrame from an assay preview is generated.
From this tutorial, we should have 2 windows of dta to look at, each one minute apart. The first window should show status: OK, with the second window with the very large house prices will show status: alert
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display the full dataframe from the analyses
assay_results.to_full_dataframe()
| window_start | analyzed_at | elapsed_millis | baseline_summary_count | baseline_summary_min | baseline_summary_max | baseline_summary_mean | baseline_summary_median | baseline_summary_std | baseline_summary_edges_0 | ... | summarizer_provided_edges | status | id | assay_id | pipeline_id | workspace_id | workspace_name | warning_threshold | bin_index | created_at | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2024-07-16T17:14:27.239563+00:00 | 2024-07-16T17:17:49.440491+00:00 | 17 | 500 | 236238.671875 | 1295531.75 | 513781.205375 | 448627.8125 | 233066.759431 | 236238.671875 | ... | None | Ok | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| 1 | 2024-07-16T17:16:27.239563+00:00 | 2024-07-16T17:17:49.440649+00:00 | 9 | 500 | 236238.671875 | 1295531.75 | 513781.205375 | 448627.8125 | 233066.759431 | 236238.671875 | ... | None | Alert | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
2 rows × 88 columns
Analysis Compare Basic Stats
The method wallaroo.assay.AssayAnalysis.compare_basic_stats returns a DataFrame comparing one set of inference data against the baseline.
This is compared to the Analysis List DataFrame, which is a list of all of the inference data split into intervals, while the Analysis Compare Basic Stats shows the breakdown of one set of inference data against the baseline.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display one analysis against the baseline
assay_results[0].compare_basic_stats()
| Baseline | Window | diff | pct_diff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 500.0 | 1000.0 | 500.000000 | 100.000000 |
| min | 236238.671875 | 236238.671875 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| max | 1295531.75 | 1489624.25 | 194092.500000 | 14.981686 |
| mean | 513781.205375 | 512779.469375 | -1001.736000 | -0.194973 |
| median | 448627.8125 | 448627.8125 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| std | 233066.759431 | 226255.370366 | -6811.389065 | -2.922506 |
| start | 2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00 | 2024-07-16T17:14:27.239563+00:00 | NaN | NaN |
| end | 2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | 2024-07-16T17:15:27.239563+00:00 | NaN | NaN |
Configure Assays
Before creating the assay, configure the assay and continue to preview it until the best method for detecting drift is set. The following options are available.
Inference Interval and Inference Width
The inference interval aka window interval sets how often to run the assay analysis. This is set from the wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.window_builder.add_interval method to collect data expressed in time units: “hours=24”, “minutes=1”, etc.
For example, with an interval of 1 minute, the assay collects data every minute. Within an hour, 60 intervals of data is collected.
We can adjust the interval and see how the assays change based on how frequently they are run.
The width sets the time period from the wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.window_builder.add_width method to collect data expressed in time units: “hours=24”, “minutes=1”, etc.
For example, an interval of 1 minute and a width of 1 minute collects 1 minutes worth of data every minute. An interval of 1 minute with a width of 5 minutes collects 5 minute of inference data every minute.
By default, the interval and width is 24 hours.
For this example, we’ll adjust the width and interval from 1 minute to 5 minutes and see how the number of analyses and their score changes.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show the analyses chart
assay_results.chart_scores()

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to five minutes each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=5).add_interval(minutes=5).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show the analyses chart
assay_results.chart_scores()

Add Run Until and Add Inference Start
For previewing assays, setting wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.add_run_until sets the end date and time for collecting inference data. When an assay is uploaded, this setting is no longer valid - assays run at the Inference Interval until the assay is paused.
Setting the wallaroo.assay_config.WindowBuilder.add_start sets the start date and time to collect inference data. When an assay is uploaded, this setting is included, and assay results will be displayed starting from that start date at the Inference Interval until the assay is paused. By default, add_start begins 24 hours after the assay is uploaded unless set in the assay configuration manually.
For the following example, the add_run_until setting is set to datetime.datetime.now() to collect all inference data from assay_window_start up until now, and the second example limits that example to only two minutes of data.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results, minus 2 minutes for the period to start gathering analyses
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start+datetime.timedelta(seconds=-120))
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show the analyses chart
assay_results.chart_scores()

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results plus 2 minutes
assay_baseline.add_run_until(assay_window_start+datetime.timedelta(seconds=120))
# Set the interval and window to one minute each
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show the analyses chart
assay_results.chart_scores()

Score Metric
The score is a distance between the baseline and the analysis window. The larger the score, the greater the difference between the baseline and the analysis window. The following methods are provided determining the score:
PSI(Default) - Population Stability Index (PSI).MAXDIFF: Maximum difference between corresponding bins.SUMDIFF: Mum of differences between corresponding bins.
The metric type used is updated with the wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.add_metric(metric: wallaroo.assay_config.Metric) method.
The following three charts use each of the metrics. Note how the scores change based on the score type used.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# set metric PSI mode
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_metric(wallaroo.assay_config.Metric.PSI)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display one analysis from the results
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.008604680420075936
scores = [0.0, 0.001015989699687698, 0.0009472210786334042, 0.0033382848156130714, 0.002503651312977887, 0.0001265890399214496, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# set metric MAXDIFF mode
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_metric(wallaroo.assay_config.Metric.MAXDIFF)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display one analysis from the results
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = MaxDiff
weighted = False
score = 0.025000000000000026
scores = [0.0, 0.014000000000000012, 0.013999999999999985, 0.025000000000000026, 0.022999999999999993, 0.0050000000000000044, 0.007]
index = 3

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# set metric SUMDIFF mode
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_metric(wallaroo.assay_config.Metric.SUMDIFF)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# display one analysis from the results
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = SumDiff
weighted = False
score = 0.04400000000000001
scores = [0.0, 0.014000000000000012, 0.013999999999999985, 0.025000000000000026, 0.022999999999999993, 0.0050000000000000044, 0.007]
index = None

Alert Threshold
Assay alert thresholds are modified with the wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.add_alert_threshold(alert_threshold: float) method. By default alert thresholds are 0.1.
The following example updates the alert threshold to 0.5.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# set the alert threshold
assay_baseline.add_alert_threshold(0.5)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show the analyses with the alert threshold
assay_results.to_dataframe()
| id | assay_id | assay_name | iopath | pipeline_id | pipeline_name | workspace_id | workspace_name | score | start | min | max | mean | median | std | warning_threshold | alert_threshold | status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | None | assays from date baseline | None | None | None | 0.008605 | 2024-07-16T17:14:27.239563+00:00 | 2.362387e+05 | 1489624.250 | 5.127795e+05 | 4.486278e+05 | 226255.370366 | None | 0.5 | Ok | ||
| 1 | None | None | assays from date baseline | None | None | None | 8.868483 | 2024-07-16T17:16:27.239563+00:00 | 1.514079e+06 | 2016006.125 | 1.881163e+06 | 1.946438e+06 | 162405.590663 | None | 0.5 | Alert |
Number of Bins
Number of bins sets how the baseline data is partitioned. The total number of bins includes the set number plus the left_outlier and the right_outlier, so the total number of bins will be the total set + 2.
The number of bins is set with the wallaroo.assay_config.UnivariateContinousSummarizerBuilder.add_num_bins(num_bins: int) method.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# update number of bins here
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_num_bins(10)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.049245130581621346
scores = [0.0, 0.0071920518112945295, 0.0011479601685666688, 0.00024635524503391294, 0.003431094801012864, 0.0005425807707100881, 0.0041791943627767685, 0.016044296997867993, 0.00495016900394247, 0.00364643113587909, 0.0071920518112945295, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

Binning Mode
Binning Mode defines how the bins are separated. Binning modes are modified through the wallaroo.assay_config.UnivariateContinousSummarizerBuilder.add_bin_mode(bin_mode: bin_mode: wallaroo.assay_config.BinMode, edges: Optional[List[float]] = None).
Available bin_mode values from wallaroo.assay_config.Binmode are the following:
QUANTILE(Default): Based on percentages. Ifnum_binsis 5 then quintiles so bins are created at the 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% points.EQUAL: Evenly spaced bins where each bin is set with the formulamin - max / num_binsPROVIDED: The user provides the edge points for the bins.
If PROVIDED is supplied, then a List of float values must be provided for the edges parameter that matches the number of bins.
The following examples are used to show how each of the binning modes effects the bins.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# update binning mode here
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_bin_mode(wallaroo.assay_config.BinMode.QUANTILE)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.008604680420075936
scores = [0.0, 0.001015989699687698, 0.0009472210786334042, 0.0033382848156130714, 0.002503651312977887, 0.0001265890399214496, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# update binning mode here
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_bin_mode(wallaroo.assay_config.BinMode.EQUAL)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Equal
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.014403886718133243
scores = [0.0, 2.0986366569212073e-06, 0.000233593237538099, 0.001922311458522506, 0.009091699485742576, 0.002481239426430717, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

The following example manually sets the bin values.
The values in this dataset run from 200000 to 1500000. We can specify the bins with the BinMode.PROVIDED and specifying a list of floats with the right hand / upper edge of each bin and optionally the lower edge of the smallest bin. If the lowest edge is not specified the threshold for left outliers is taken from the smallest value in the baseline dataset.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
edges = [200000.0, 400000.0, 600000.0, 800000.0, 1500000.0, 2000000.0]
# update binning mode here
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_bin_mode(wallaroo.assay_config.BinMode.PROVIDED, edges)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Provided
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.005462658417539512
scores = [0.0, 0.0002882043853549172, 0.0017843411661165069, 5.438215377767015e-05, 0.003335730712290418, 0.0, 0.0]
index = None

Aggregation Options
Assay aggregation options are modified with the wallaroo.assay_config.AssayBuilder.add_aggregation(aggregation: wallaroo.assay_config.Aggregation) method. The following options are provided:
Aggregation.DENSITY(Default): Count the number/percentage of values that fall in each bin.Aggregation.CUMULATIVE: Empirical Cumulative Density Function style, which keeps a cumulative count of the values/percentages that fall in each bin.
The following example demonstrate the different results between the two.
# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
#Aggregation.DENSITY - the default
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_aggregation(wallaroo.assay_config.Aggregation.DENSITY)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Density
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.008604680420075936
scores = [0.0, 0.001015989699687698, 0.0009472210786334042, 0.0033382848156130714, 0.002503651312977887, 0.0001265890399214496, 0.0006729444732424258]
index = None

# Create the assay baseline
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# Set the assay parameters
# The end date to gather inference results
assay_baseline.add_run_until(datetime.datetime.now())
# Set the interval and window to one minute each, set the start date for gathering inference results
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
#Aggregation.CUMULATIVE
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_aggregation(wallaroo.assay_config.Aggregation.CUMULATIVE)
# build the assay configuration
assay_config = assay_baseline.build()
# perform an interactive run and collect inference data
assay_results = assay_config.interactive_run()
# show one analysis with the updated bins
assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Cumulative
metric = PSI
weighted = False
score = 0.04800000000000004
scores = [0.0, 0.014000000000000012, 0.0, 0.025000000000000026, 0.0020000000000000018, 0.007000000000000006, 0.0]
index = None

Create Assay
With the assay previewed and configuration options determined, we officially create it by uploading it to the Wallaroo instance.
Once it is uploaded, the assay runs an analysis based on the window width, interval, and the other settings configured.
Assays are uploaded with the wallaroo.assay_config.upload() method. This uploads the assay into the Wallaroo database with the configurations applied and returns the assay id. Note that assay names must be unique across the Wallaroo instance; attempting to upload an assay with the same name as an existing one will return an error.
wallaroo.assay_config.upload() returns the assay id for the assay.
Typically we would just call wallaroo.assay_config.upload() after configuring the assay. For the example below, we will perform the complete configuration in one window to show all of the configuration steps at once before creating the assay.
# Build the assay, based on the start and end of our baseline time,
# and tracking the output variable index 0
assay_baseline = wl.build_assay(assay_name="assays from date baseline tutorial 2",
pipeline=mainpipeline,
iopath="output variable 0",
baseline_start=assay_baseline_start,
baseline_end=assay_baseline_end)
# set the width, interval, and assay start date and time
assay_baseline.window_builder().add_width(minutes=1).add_interval(minutes=1).add_start(assay_window_start)
# add other options
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_aggregation(wallaroo.assay_config.Aggregation.CUMULATIVE)
assay_baseline.summarizer_builder.add_metric(wallaroo.assay_config.Metric.MAXDIFF)
assay_baseline.add_alert_threshold(0.5)
assay_id = assay_baseline.upload()
# wait 65 seconds for the first analysis run performed
time.sleep(65)
The assay is now visible through the Wallaroo UI by selecting the workspace, then the pipeline, then Insights.
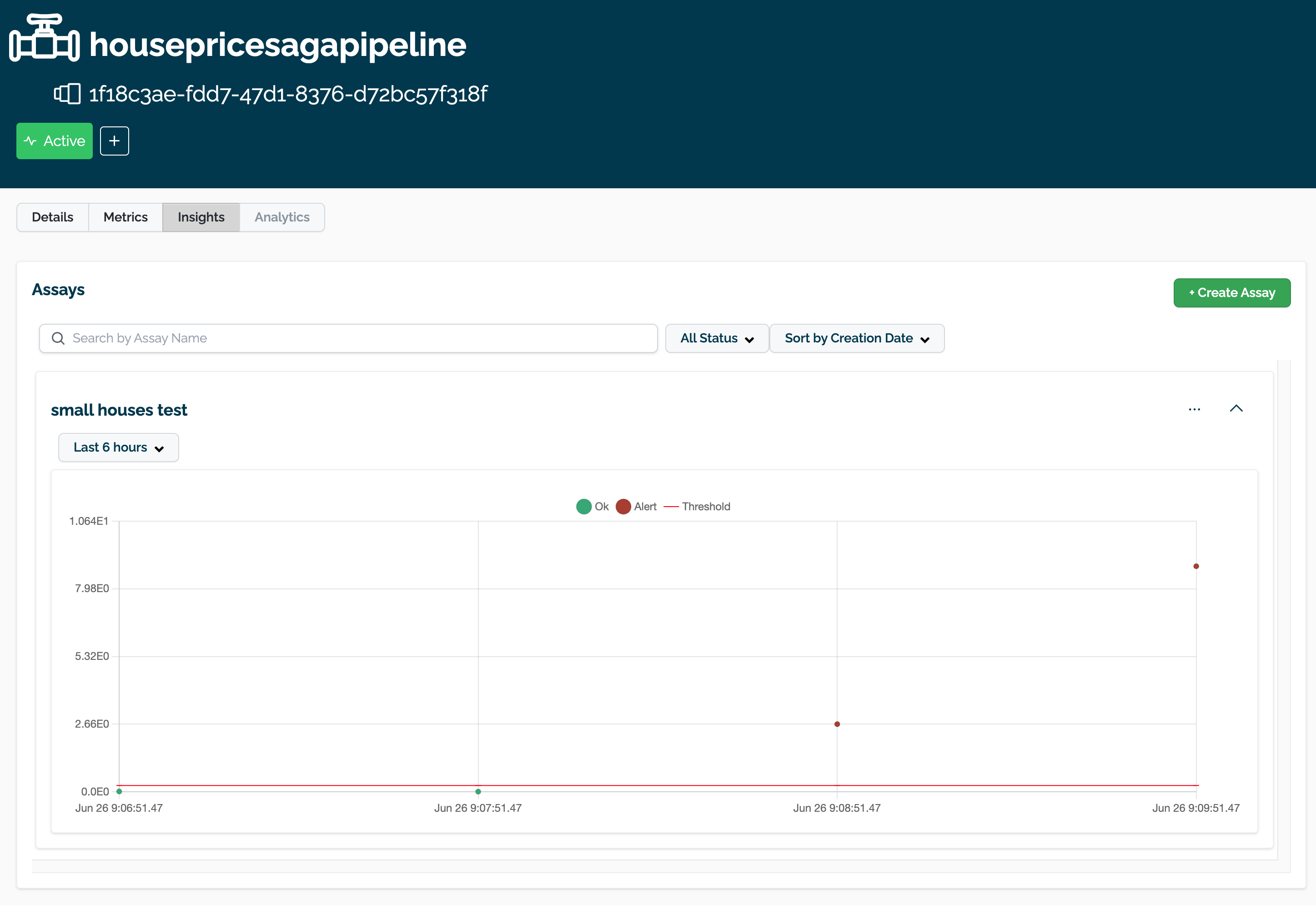
Get Assay Info
Assay information is retrieved with the wallaroo.client.get_assay_info() which takes the following parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assay_id | Integer (Required) | The numerical id of the assay. |
| workspace_id | (Int) (Optional) | The numerical identifier of the workspace to filter by. |
| workspace_name | (String) (Optional) | The name of the workspace to filter by. |
This returns the following:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | Integer | The numerical id of the assay. |
| name | String | The name of the assay. |
| active | Boolean | True: The assay is active and generates analyses based on its configuration. False: The assay is disabled and will not generate new analyses. |
| pipeline_name | String | The name of the pipeline the assay references. |
| last_run | DateTime | The date and time the assay last ran. |
| next_run | DateTime | THe date and time the assay analysis will next run. |
| alert_threshold | Float | The alert threshold setting for the assay. |
| baseline | Dict | The baseline and settings as set from the assay configuration. |
| iopath | String | The iopath setting for the assay. |
| metric | String | The metric setting for the assay. |
| num_bins | Integer | The number of bins for the assay. |
| bin_weights | List/None | The bin weights used if any. |
| bin_mode | String | The binning mode used. |
| workspace_id | (Int) | The numerical identifier of the workspace the assay is associated with. |
| workspace_name | (String) | The name of the workspace the assay is associated with. |
display(wl.get_assay_info(assay_id))
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484407+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:41:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
Get Assay Results
Once an assay is created the assay runs an analysis based on the window width, interval, and the other settings configured.
Assay results are retrieved with the wallaroo.client.get_assay_results method which takes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assay_id | Integer (Required) | The numerical id of the assay. |
| start | Datetime.Datetime (Required) | The start date and time of historical data from the pipeline to start analyses from. |
| end | Datetime.Datetime (Required) | The end date and time of historical data from the pipeline to limit analyses to. |
| workspace_id | (Int) (Optional) | The numerical identifier of the workspace to filter by. |
| workspace_name | (String) (Optional) | The name of the workspace to filter by. |
Admin users have unrestricted access to all workspaces. For more details, see Wallaroo Enterprise User Management.
- IMPORTANT NOTE: This process requires that additional historical data is generated from the time the assay is created to when the results are available. To add additional inference data, use the Assay Test Data section above.
assay_results = wl.get_assay_results(assay_id=assay_id,
start=assay_window_start,
end=datetime.datetime.now())
assay_results.chart_scores()

assay_results[0].chart()
baseline mean = 513781.205375
window mean = 512779.469375
baseline median = 448627.8125
window median = 448627.8125
bin_mode = Quantile
aggregation = Cumulative
metric = MaxDiff
weighted = False
score = 0.025
scores = [0.0, 0.014000000000000012, 0.0, 0.025000000000000026, 0.0020000000000000018, 0.007000000000000006, 0.0]
index = 3

List Assays
A list of assays is retrieved with the wallaroo.client.list_assays() method and takes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| workspace_id | (Int) (Optional) | The numerical identifier of the workspace to filter by. |
| workspace_name | (String) (Optional) | The name of the workspace to filter by. |
This returns a list of assays as filtered in reverse chronological order.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Assay Id | Integer | The numerical id of the assay. |
| Assay Name | String | The name of the assay. |
| Active | Boolean | True: The assay is active and generates analyses based on its configuration. False: The assay is disabled and will not generate new analyses. |
| Status | Dict | The status of the assay including the |
| Warning Threshold | Float/None | The warning threshold if set. |
| Alert Threshold | Float | The alert threshold for the assay. |
| Pipeline Id | Integer | The numerical id of the pipeline the assay references. |
| Pipeline Name | String | The name of the pipeline the assay references. |
| workspace_id | (Int) | The numerical identifier of the workspace the assay is associated with. |
| workspace_name | (String) | The name of the workspace the assay is associated with. |
The errors for this method include:
- If the parameter
workspace_idis not an integer. - If the parameter
workspace_nameis not a String.
wl.list_assays()
| Assay ID | Assay Name | Active | Status | Warning Threshold | Alert Threshold | Pipeline ID | Pipeline Name | Workspace ID | Workspace Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484407+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 28 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 |
| 1 | assays from date baseline tutorial | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T17:08:02.913332768+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 24 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 27 | assay-demonstration-tutorial |
Set Assay Active Status
Assays active status is either:
- True: The assay generates analyses based on the assay configuration.
- False: The assay will not generate new analyses.
Assays are set to active or not active with the wallaroo.client.set_assay_active which takes the following parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assay_id | Integer | The numerical id of the assay. |
| active | Boolean | True: The assay status is set to Active. False: The assay status is Not Active. |
First we will show the current active status.
In the following, set the assay status to False, then set the assay active status back to True.
display(wl.get_assay_info(assay_id))
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484407+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:41:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
Now we set the active status to False, and show the assay list to verify it is no longer active.
wl.set_assay_active(assay_id, False)
display(wl.get_assay_info(assay_id))
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | False | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484407+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:41:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
We resume the assay by setting it’s active status to True.
wl.set_assay_active(assay_id, True)
display(wl.get_assay_info(assay_id))
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484407+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:42:03.041484+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:41:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
View Assay Filters
The following examples demonstrate various ways of listing assays and retrieving assay details, with filtering options.
List Assays with Filters
List all assays for workspaces the user is a member of.
wl.list_assays()
| Assay ID | Assay Name | Active | Status | Warning Threshold | Alert Threshold | Pipeline ID | Pipeline Name | Workspace ID | Workspace Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:29:03.024210200+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 28 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 |
| 1 | assays from date baseline tutorial | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T17:08:02.913332768+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 24 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 27 | assay-demonstration-tutorial |
List all assays filtered by workspace id.
wl.list_assays(workspace_id=27)
| Assay ID | Assay Name | Active | Status | Warning Threshold | Alert Threshold | Pipeline ID | Pipeline Name | Workspace ID | Workspace Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | assays from date baseline tutorial | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T17:08:02.913332768+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 24 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 27 | assay-demonstration-tutorial |
List assays filtered by workspace name.
wl.list_assays(workspace_name="assay-demonstration-tutorial-2")
| Assay ID | Assay Name | Active | Status | Warning Threshold | Alert Threshold | Pipeline ID | Pipeline Name | Workspace ID | Workspace Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:30:03.029976427+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | None | 0.5 | 28 | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 |
Get Assay Results
Get assay results.
assay_results = wl.get_assay_results(assay_id=assay_id,
start=assay_window_start,
end=datetime.datetime.now())
assay_results.chart_scores()

Get assay results filtered by workspace id.
assay_results = wl.get_assay_results(assay_id=assay_id,
workspace_id=29,
start=assay_window_start,
end=datetime.datetime.now())
assay_results.chart_scores()

Get assay results filtered by workspace name.
assay_results = wl.get_assay_results(assay_id=assay_id,
workspace_name="assay-demonstration-tutorial-2",
start=assay_window_start,
end=datetime.datetime.now())
assay_results.chart_scores()

Get Assay Info
Get assay info.
wl.get_assay_info(assay_id=assay_id)
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:35:03.031351761+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:35:03.031352+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:34:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
Get assay info filtered by workspace id.
wl.get_assay_info(assay_id=assay_id,
workspace_id=29)
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:36:03.030744191+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:36:03.030744+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:35:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |
Get assay info filtered by workspace name.
wl.get_assay_info(assay_id=assay_id,
workspace_name="assay-demonstration-tutorial-2")
| id | name | active | status | pipeline_name | last_run | next_run | alert_threshold | workspace_id | workspace_name | baseline | iopath | metric | num_bins | bin_weights | bin_mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | assays from date baseline tutorial 2 | True | {"run_at": "2024-07-16T18:36:03.030744191+00:00", "num_ok": 0, "num_warnings": 0, "num_alerts": 0} | assay-demonstration-tutorial | 2024-07-16T18:36:03.030744+00:00 | 2024-07-16T18:35:27.239563+00:00 | 0.5 | 29 | assay-demonstration-tutorial-2 | Start:2024-07-16T17:12:27.123262+00:00, End:2024-07-16T17:13:27.222262+00:00 | output variable 0 | MaxDiff | 5 | None | Quantile |