Persistent Storage Nodepools
Table of Contents
Installations of Wallaroo use persistent storage for the following services:
minio: Used to storage ML models for deployment.postgres: Used to store configurations and settings.plateau: A custom Wallaroo service to store inference results.jupyter: JupyterHub and JupyterLab for running Jupyter Notebooks within the Wallaroo environment.prometheus: Provides Prometheus monitoring to track cluster performance.
By default, these services are deployed to Kubernetes nodepool with the following taints and labels applied.
| Nodepool | Taints | Labels | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| persistent | wallaroo.ai/persistent=true:NoSchedule | wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent | For Wallaroo services with a persistentVolume settings, including JupyterHub, Minio, etc. |
If the taints and labels for the nodepool are altered, verify that tolerations and nodeSelector settings for the service match.
For the Kubernetes cluster hosting the Wallaroo instance, see the documentation for the hosting for instructions on setting or updating the persistent volume storage capacity to handle the requested storage capacity.
Setting Storage for Kots Installations
For installs of Wallaroo via kots, the following procedures are used to update the storage and resource capacity for persistent storage services.
The following prerequisites must be met:
- Access to the Kubernetes environment running the Wallaroo instances.
- Have
kubectlandkotsinstalled and connected to the Kubernetes environment.
For full details on installing Wallaroo and the prerequisite software, see the Wallaroo Prerequisites Guide.
- Access the Kots Administrative Dashboard.
From a terminal with
kubectlandkotsinstalled and connected to the Kubernetes environment, run:kubectl kots admin-console --namespace wallarooThis will provide access to the Kots Administrative Dashboard through
http://localhost:8800:• Press Ctrl+C to exit • Go to http://localhost:8800 to access the Admin ConsoleLaunch a browser and connect to
http://localhost:8800.Enter the password created during the Wallaroo Install process. The Kots Administrative Dashboard will now be available.
- Select Config. Select the service to update. Multiple services can be updated before deployment. When finished, scroll to the bottom and select Save config, then Go to updated version, then Deploy the latest configuration.
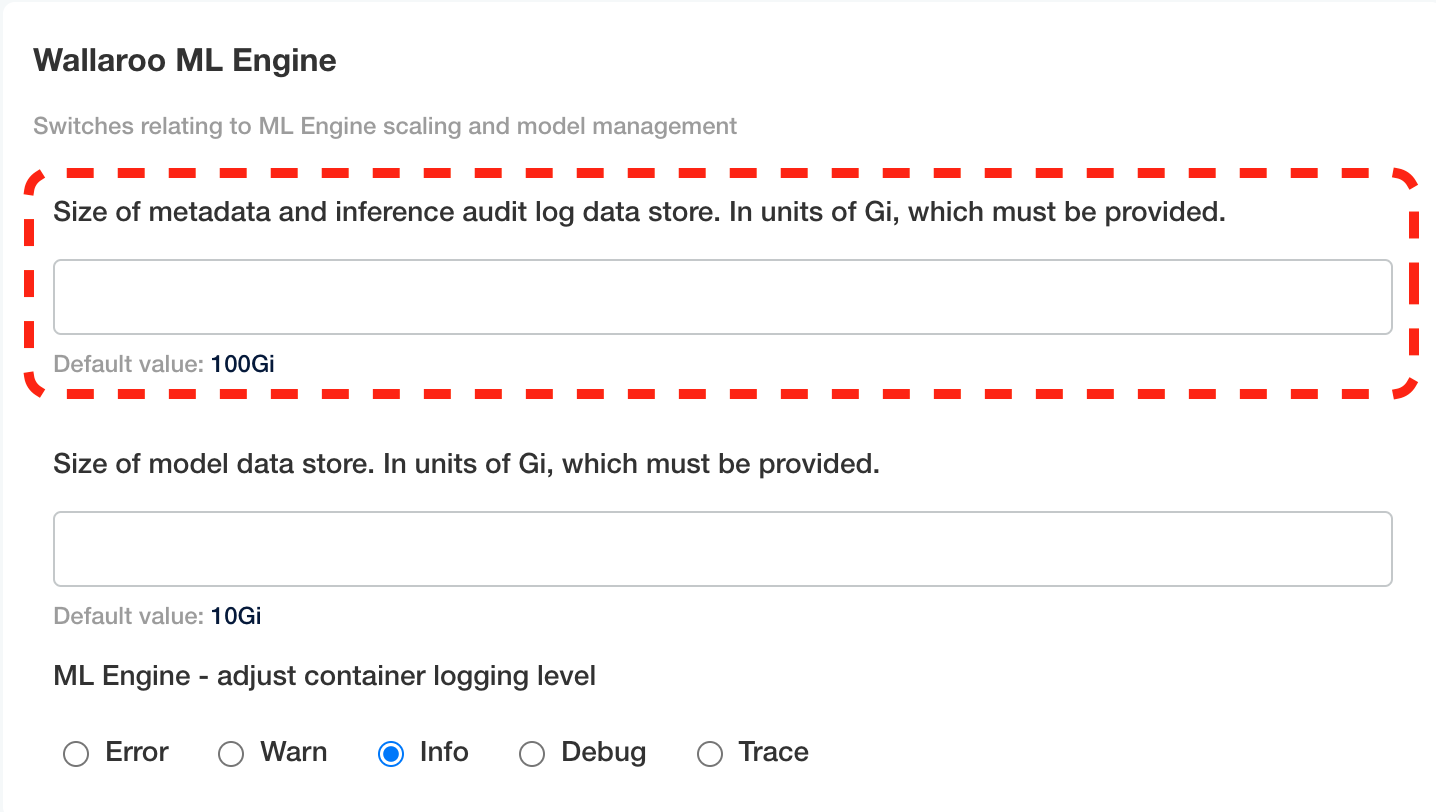
postgres: Update Wallaroo ML Engine->Size of metadata and inference audit log data store. In units of Gi, which must be provided. Update the storage capacity in terms of Gi. By default, this is 100Gi.
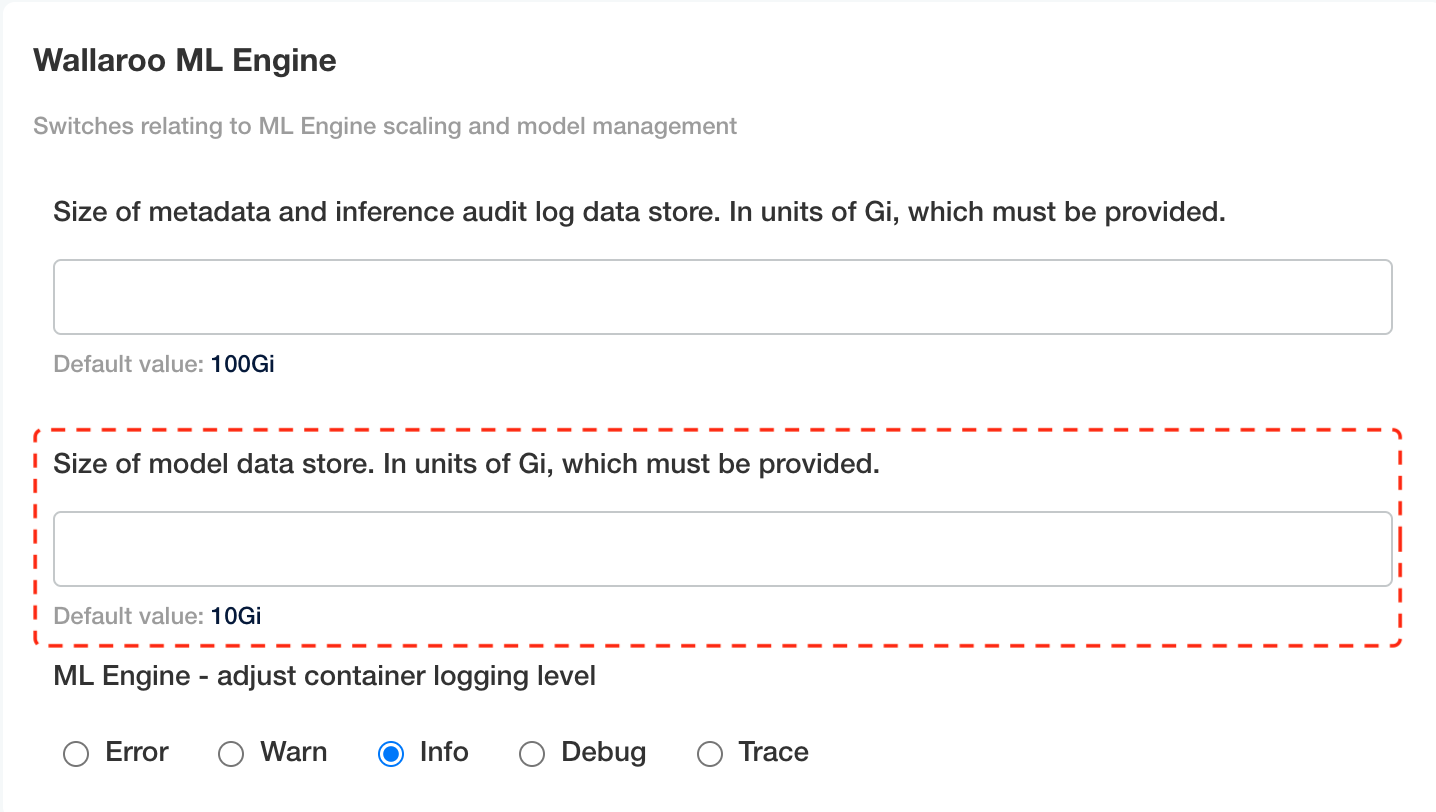
minio: Update Wallaroo ML Engine->Size of model data store. In units of Gi, which must be provided. Update the storage capacity in terms of Gi. By default, this is 10Gi.
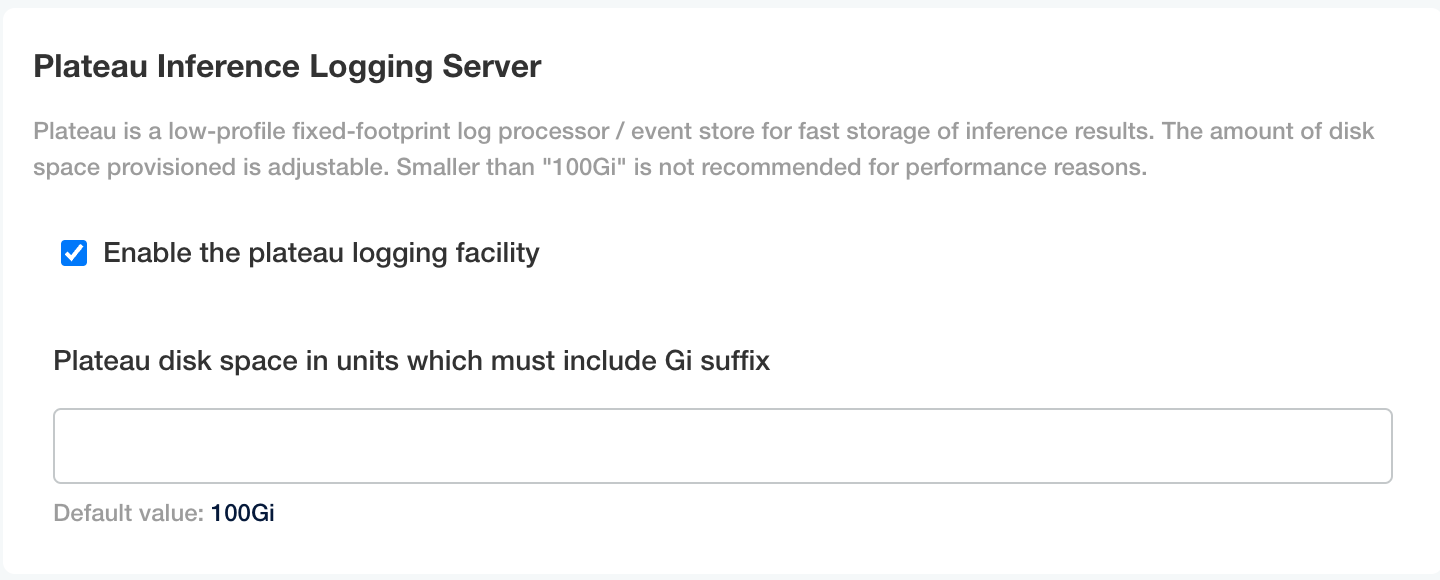
plateau: Plateau Inference Logging Server: Set Plateau disk space in units which must include Gi suffix. Default is 100Gi
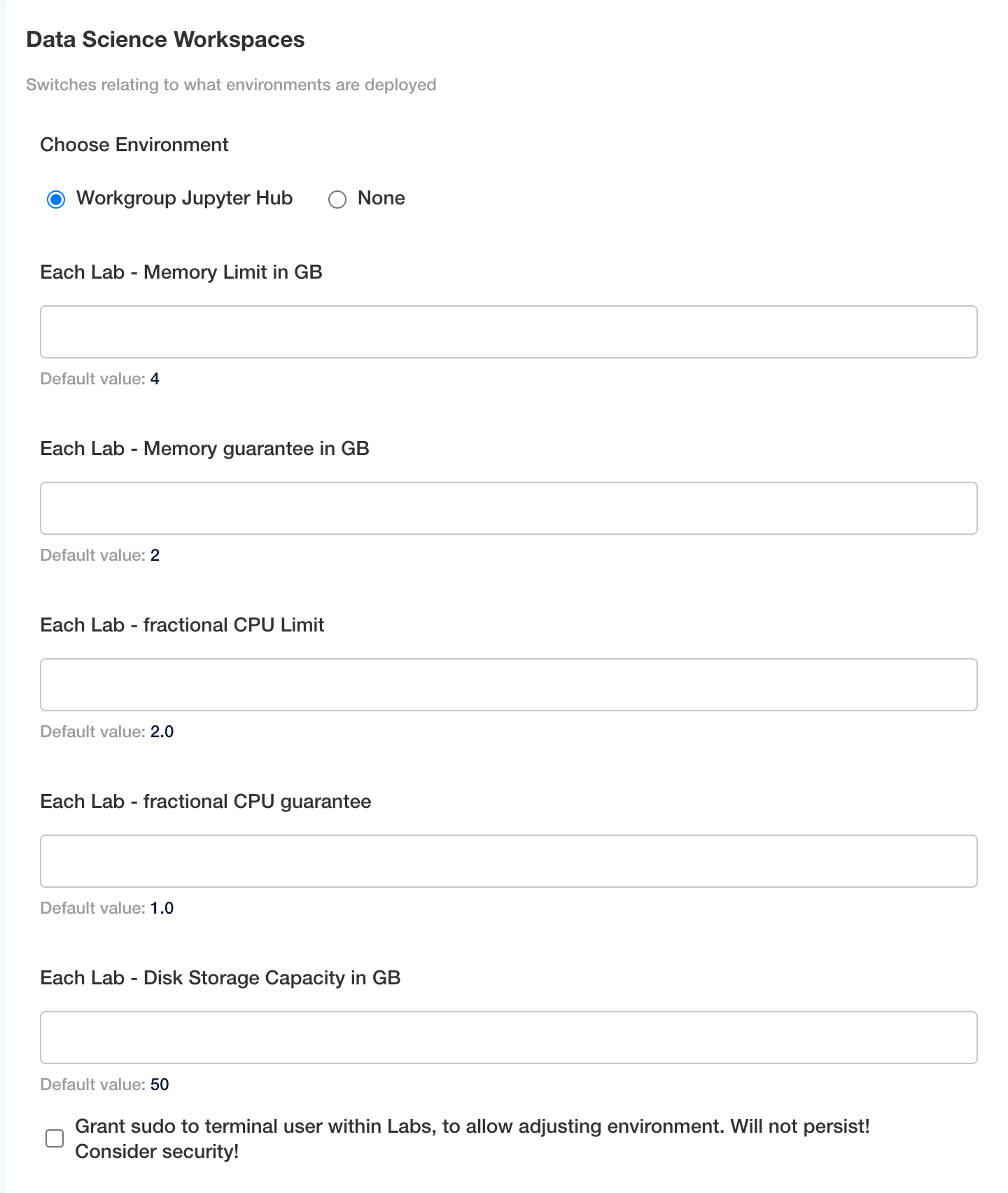
jupyter: Data Science Workspaces: Update the memory limits and disk storage capacity for each lab deployed. This allocates these resources for each JupyterHub user with their own lab.
Setting Storage for Helm Installations
The following snippets show how to set the storage capacity for each service. Adjust the disk size and resources as required.
The following code snippet shows updating the storage capacity for the minio service. Adjust the resources and diskSize as needed, and verify the nodeSelector matches the nodepool label and the tolerations matches the nodepool taint where the service is deployed to.
minio:
persistence:
size: 25Gi
nodeSelector:
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
tolerations:
- key: wallaroo.ai/persistent
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
The following code snippet shows updating the storage capacity for the postgres service. Adjust the resources and diskSize as needed, and verify the nodeSelector matches the nodepool label and the tolerations matches the nodepool taint where the service is deployed to.
postgres:
diskSize: 10Gi
nodeSelector:
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
tolerations:
- key: "wallaroo.ai/persistent"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
resources:
limits:
memory: 2Gi
cpu: 500m
requests:
memory: 512Mi
cpu: 100m
The following code snippet shows updating the storage capacity for the plateau service. Adjust the resources and diskSize as needed, and verify the nodeSelector matches the nodepool label and the tolerations matches the nodepool taint where the service is deployed to.
plateau:
diskSize: 100Gi
resources:
limits:
memory: 4Gi
cpu: 1000m
requests:
memory: 128Mi
cpu: 100m
nodeSelector:
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
tolerations:
- key: "wallaroo.ai/persistent"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
The following code snippet shows updating the storage capacity for the prometheus service. Adjust the storageRetentionTimeDays and storageRetentionSizeGb as needed, and verify the nodeSelector matches the nodepool label and the tolerations matches the nodepool taint where the service is deployed to.
prometheus:
storageRetentionSizeGb: "10" # Retain this much data, in GB.
storageRetentionTimeDays: "15" # When to remove old data. In days.
nodeSelector:
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
tolerations:
- key: "wallaroo.ai/persistent"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
resources:
limits:
memory: 6Gi
cpu: 2000m
requests:
memory: 512Mi
cpu: 100m
The following snippet is used in helm values files to set the storage for the jupyter service. Modify the nodeSelector, tolerations, labNodeSelector and labTolerations match the taints and labels for the nodepool the service is deployed on.
# Jupyter has both hub and lab nodeSelectors and tolerations
# They default to the same persistent pool, but can be assigned to different ones
jupyter:
nodeSelector: # Node placement for Hub administrative pods
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
tolerations:
- key: "wallaroo.ai/persistent"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
labNodeSelector: # Node placement for Hub-spawned jupyterlab pods
wallaroo.ai/node-purpose: persistent
labTolerations:
- key: "wallaroo.ai/persistent"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
memory:
limit: "4" # Each Lab - memory limit in GB
guarantee: "2" # Each Lab - lemory guarantee in GB
cpu:
limit: "2.0" # Each Lab - fractional CPU limit
guarantee: "1.0" # Each Lab - fractional CPU guarantee
storage:
capacity: "50" # Each Lab - disk storage capacity in GB