How to update SSL Certificates for Wallaroo
Generate Certificates
The following settings are used for TLS certificates.
- Create a CA-signed TLS certificate for your Wallaroo domain with the following settings:
- Certificate Authority Options:
- Use a public Certificate Authority such as Let’s Encrypt or Verisign. In general, you would send a Certificate Signing Request to your CA and they would respond with your certificates.
- Use a private Certificate Authority (CA) to provide the certificates. Your organization will have procedures for clients to verify the certificates from the private CA.
- Use a Wallaroo certificate and public name server. Contact our CSS team for details.
- Subject Domain:
- Set the certificate’s Subject CN to your Wallaroo domain.
- With Wildcards: To use wildcards, use the wildcard
*.{suffix domain}. For example, if the domain suffix iswallaroo.example.com, then the Subject CNs would be:- wallaroo.example.com
- *.wallaroo.example.com
- If wildcard domains are not desired, use a combination of Subject and Subject Alternative Names to set names as follows:
wallaroo.example.comapi.wallaroo.example.comjupyter.wallaroo.example.comkeycloak.wallaroo.example.com
- With Wildcards: To use wildcards, use the wildcard
- Set the certificate’s Subject CN to your Wallaroo domain.
- Save your certificates.
- You should have two files: the TLS Certificate (
.crt) and TLS private key (.key). Store these in a secure location - these will be installed into Wallaroo at a later step.
- You should have two files: the TLS Certificate (
- Certificate Authority Options:
Update SSL Certificates for Kots Installations
The following is for updating SSL certificates in Wallaroo for a Kots based installation.
Access the Kots Administrative Dashboard in your browser. This can be done either after installation, or through the following command (assuming your Wallaroo instance was installed into the namespace
wallaroo). By default this provides the Kots Administrative Dashboard through the URLhttps://localhost:8800.kubectl kots admin-console --namespace wallarooFrom the Wallaroo Dashboard, select Config and set the following:
TLS Certificates
- Use custom TLS Certs: Checked
- TLS Certificate: Enter your TLS Certificate (.crt file).
- TLS Private Key: Enter your TLS private key (.key file).
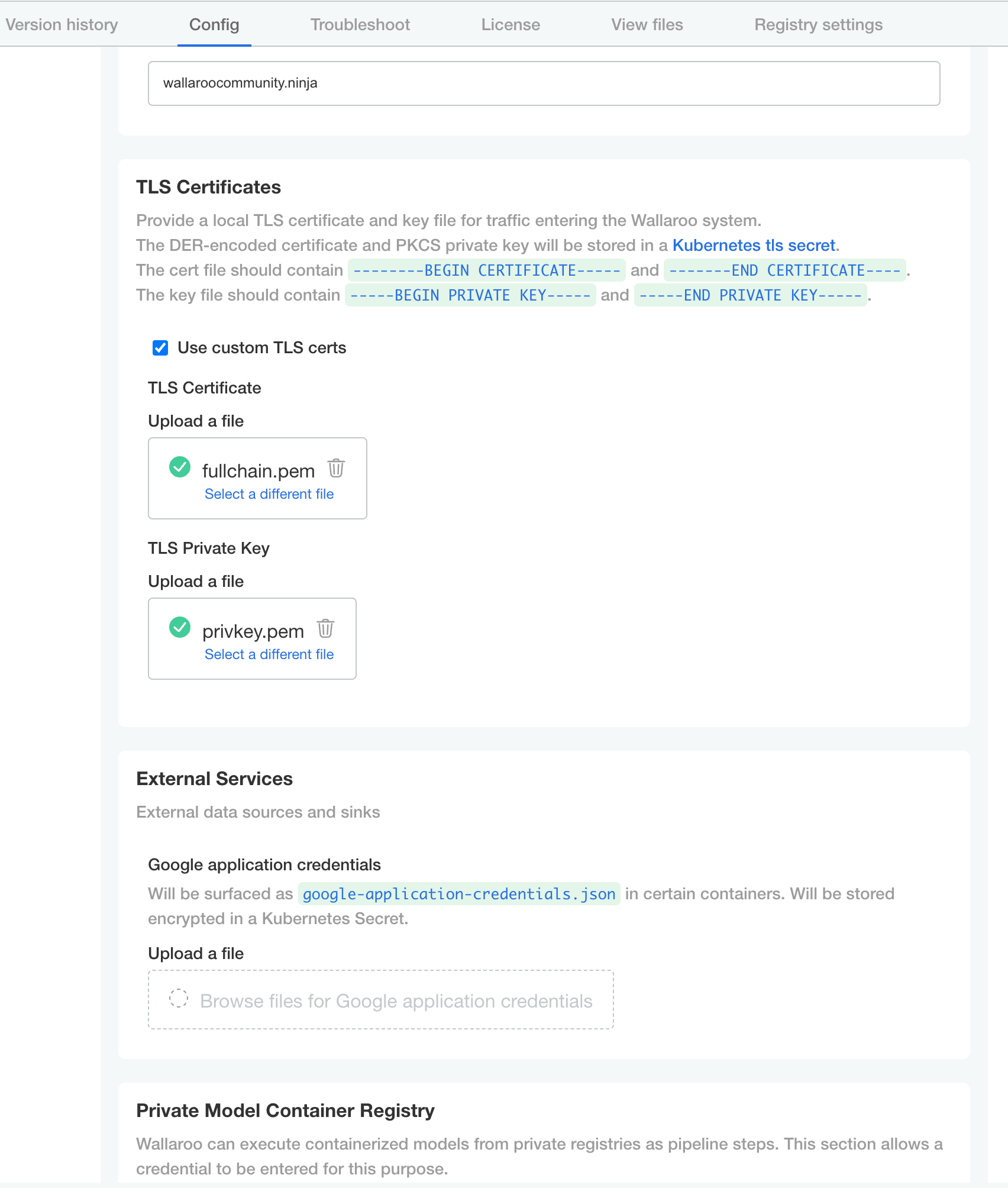
Once complete, scroll to the bottom of the Config page and select Save config.
A pop-up window will display The config for Wallaroo Enterprise has been updated.. Select Go to updated version to continue.
From the Version History page, select Deploy. Once the new deployment is finished, you will be able to access your Wallaroo services via their DNS addresses.
Update SSL Certificates for Helm Installations
SSL certificates for Helm based installations of Wallaroo are stored as Kubernetes secrets. SSL certificates are set during the Wallaroo install procedure. The following procedure defines how to update the secret key with new TLS certificates.
Create Kubectl Secret from Certificates
The following creates a new Kubectl secret from the SSL certificates. This is used when old certificates are expired or new certificates generated by a different certificate authority are used.
Set the default Kubernetes namespace to the one the Wallaroo instance is installed to. By default,
wallaroo. For example:kubectl config set-context --current --namespace wallarooCreate a new Kubernetes secret to the same namespace as the Wallaroo instance, using the TLS Certificate and TLS private key. For example, the following command creates the secret from the variable
$TLSCONFIGfrom the certificate file stored in the variable$TLSSECRETSand the private key stored in the variable$TLSSECRETS, with Wallaroo installed to the namespacewallaroo. IMPORTANT NOTE: Creating a Kubernetes secret in the same namespace with the same name as an already existing Kubernetes secret generates an error.kubectl create secret tls $TLSCONFIG --cert=$TLSSECRETS --key=$TLSSECRETSFor example, if new
$TLSCONFIGiscust-cert-secretwithexample.com.crtand keyexample.com.key, then the command would be translated askubectl create secret tls cust-cert-secret --cert=example.com.crt --key=example.com.key --namespace wallarooUpdate the
local-values.yamlfile with the new Kubernetes secret set to thecustTlsSecretNameHelm variable. The following is a minimum settinglocal-values.yamlfile. For details on otherhelmbased settings, see the Wallaroo Helm Reference Guides.
domainPrefix: "" # optional if using a DNS Prefix
domainSuffix: "wallaroo.example.com"
custTlsSecretName: cust-cert-secret
apilb:
serviceType: LoadBalancer
external_inference_endpoints_enabled: true
ingress_mode: internal # internal (Default), external,or none
dashboard:
clientName: "Wallaroo Helm Example" # Insert the name displayed in the Wallaroo Dashboard
kubernetes_distribution: "" # Required. One of: aks, eks, gke, oke, or kurl.
Update Helm
Update the
helmbased installation with thehelm upgradecommand in the following format:helm upgrade $RELEASE $REGISTRYURL --version $VERSION --values $LOCALVALUES.yamlWhere:
$RELEASE: The name of the Helm release. By default, wallaroo.$REGISTRYURL: The URl for the Wallaroo container registry service.$VERSION: The version of Wallaroo to install. For this example,2024.1.0-5097.$LOCALVALUES: The .yaml file containing the local values overrides. For this example,local-values.yaml.
For example, for the registration
wallaroothe command would be:helm upgrade wallaroo oci://registry.replicated.com/wallaroo/2024-1/wallaroo --version 2024.1.0-5097 --values local-values.yamlDelete the old Kubernetes secret used to store the TLS certificates with the following command format, where
$OLDTLSCONFIGis the old secret name, and `$:kubectl delete secret $TLSCONFIG
Once the new deployment is finished, you will be able to access your Wallaroo services via their DNS addresses.